The healthcare landscape is continually developing, driven by progressions in clinical innovation, advancing guidelines, and arising illness dangers. While these progressions offer enormous advantages in LMS for Healthcare, they likewise make a critical requirement for an exceptionally talented and versatile labor force fit for staying up with these changes. Traditionally, staying up with the latest depended on paper-based materials and in-person seminars, which are in many cases tedious, costly, and hard to make due.
As per a 2023 report by the American Emergency clinic Affiliation, 72% of healthcare chiefs distinguished continuous staff instruction as a first concern. However, traditional training methods frequently battle to stay up with these requests. Here’s where Learning Management Systems for Healthcare arise as a strong solution. A LMS is a software platform intended to make due, convey, and track worker learning and development programs. Explicitly tailored for the healthcare industry, these systems offer a scope of elements to address the exceptional challenges sought by healthcare Learning and Development (L&D) groups.
In this article, we’ll investigate how LMS for Healthcare can engage your association to beat four key L&D obstacles in 2024: guaranteeing consistency, arriving at a scattered labor force, tending to information holes, and estimating training viability. By utilizing the capacities of a LMS for Healthcare, custom software development services USA can develop an exceptional and certain labor force, at last prompting work on tolerant consideration and hierarchical achievement.
Ready to Build Your Own LMS Software? Let’s Create Your Software Solution Today!
Introduction to Learning Management Systems (LMS) for Healthcare
The reception of innovative technologies is fundamental for improving the proficiency, adequacy, and nature of patient consideration. One such technology that has gained critical unmistakable quality as of late is the Learning Management System (LMS). Initially produced for instructive establishments, LMS systems for healthcare have now found far and wide application in the healthcare area, offering tailored solutions to the exceptional challenges looked by healthcare associations in training and fostering their labor force.
1. Rising Demand for Continuous Education
Firstly, The healthcare industry, right off the bat, is portrayed by fast headways in clinical information, technologies, and treatment modalities. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global healthcare education solutions market size is projected to reach USD 15.8 billion by 2025. Driven by the rising interest for persistent schooling among healthcare experts to stay up with these developments.
2. Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Secondly, Healthcare experts are dependent upon severe administrative guidelines and prerequisites, requiring customary training and certificates to maintain consistency. According to a survey by HealthStream, 93% of healthcare organizations consider compliance training as a high priority. Featuring the critical job of training drives in gathering administrative commitments.
3. Workforce Development Challenges
Healthcare associations face different labor force development challenges, including high turnover rates, staffing deficiencies, and ability holes. According to a study published in the Journal of Nursing Regulation, turnover rates among registered nurses in the United States range from 8.8% to 37.0%, underscoring the need for effective training and development programs to attract, retain, and upskill healthcare professionals.
4. Advancements in Technology
The healthcare industry is seeing quick headways in clinical technology, for example, electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine platforms, and artificial intelligence (AI) applications. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global telemedicine market size is expected to reach USD 175.5 billion by 2026, driven by the increasing adoption of telehealth solutions for remote patient monitoring, consultation, and diagnosis.
5. Shift Towards Digital Learning
With the expansion of computerized technologies and the developing commonness of remote work and distance learning. There is a huge shift towards computerized learning solutions in the healthcare area. According to a survey by Docebo, 68% of custom software development outsourcing companies are planning to increase their investment in e-learning technologies, indicating a growing recognition of the benefits of digital learning platforms such as LMS for Healthcare.
Considering these patterns and challenges, the execution of Learning Management Systems (LMS) tailored explicitly for the healthcare industry offers an essential way to deal with tending to the developing training and development needs of healthcare experts. These platforms give a unified center to coordinating, conveying, and following training content. Empowering healthcare associations to upgrade labor force capability, further develop consistence results, and eventually, convey better quiet consideration.
Understanding The Importance of Healthcare Education
Ensuring a thoroughly prepared and learned labor force is as of now not an extravagance, yet an outright need. Successful healthcare schooling goes past essentially procuring specialized abilities; it engages experts to convey the greatest consideration conceivable, explore complex clinical circumstances, and cultivate positive patient collaborations.
Here is a breakdown of ten key justifications for why healthcare schooling assumes such a pivotal part in molding the fate of medication:
1. Improved Patient Outcomes
Firstly, At the heart of healthcare lies the fundamental goal of improving patient well-being. Training furnishes healthcare experts with the most recent clinical information, treatment conventions, and best works on, empowering them to settle on informed choices and give powerful consideration. Studies have shown a reasonable connection between knowledgeable healthcare experts. Worked on understanding results, including decreased death rates and higher treatment achievement rates.
2. Enhanced Quality of Care
Secondly, Education extends beyond clinical skills, encompassing areas like communication, empathy, and cultural competency. By cultivating these abilities, healthcare experts can give all encompassing consideration that tends to the actual necessities as well as the close to home and social prosperity of their patients. This accentuation on persistent focused care prompts higher patient fulfillment and confidence in the healthcare system.
3. Addressing Public Health Challenges
As the healthcare landscape wrestles with new general wellbeing dangers like arising irresistible sicknesses and constant disease, training assumes a crucial part. Extensive training outfits experts with the information and abilities to forestall, analyze, and deal with these circumstances actually. Taught healthcare experts can likewise assume a critical part in advancing general wellbeing drives with medical billing and coding software solutions and empowering patients to lead healthier lives.
4. Keeping Pace with Medical Advancements
The field of medication is continually developing, with new technologies and medicines arising at a fast speed. Nonstop schooling guarantees healthcare experts keep awake to-date on the most recent progressions. Permitting them to coordinate new methodologies and procedures into their training.
5. Reduced Medical Errors
Training assumes a critical part in limiting clinical blunders, a serious worry in healthcare. By outfitting experts with the important information and abilities, instructive projects can assist with lessening prescription mistakes. To work on symptomatic exactness, and guarantee protected and successful operations.
6. Promoting Evidence-Based Medicine
Current healthcare depends vigorously on proof based rehearses, got from thorough logical examination. Schooling prepares healthcare experts to critically assess clinical data, recognize best practices in light of proof, and apply these discoveries in their daily work.
7. Professional Development and Career Advancement
Consistent training is fundamental for healthcare experts looking to propel their professions. By procuring new abilities and skill through instructive projects, experts can expand their vocation prospects and take on positions of authority inside the healthcare system.
8. Maintaining Professional Licensure
Numerous healthcare callings require continuous schooling for licensure restoration. The healthcare learning management system guarantees experts maintain their insight base and consent to administrative necessities for proceeding with training.
9. Boosting Staff Morale and Retention
Admittance to quality instructive open doors can be a critical inspiration for healthcare experts. Organizations that focus on schooling exhibit a promise to staff development. Which can prompt expanded work fulfillment, further developed spirit, and diminished staff turnover.
10. Building a Stronger Healthcare System
At last, putting resources into healthcare instruction benefits individual experts and patients, however the whole healthcare system in general. A knowledgeable labor force prompts better quality consideration, works on understanding results, and a more effective healthcare system generally.
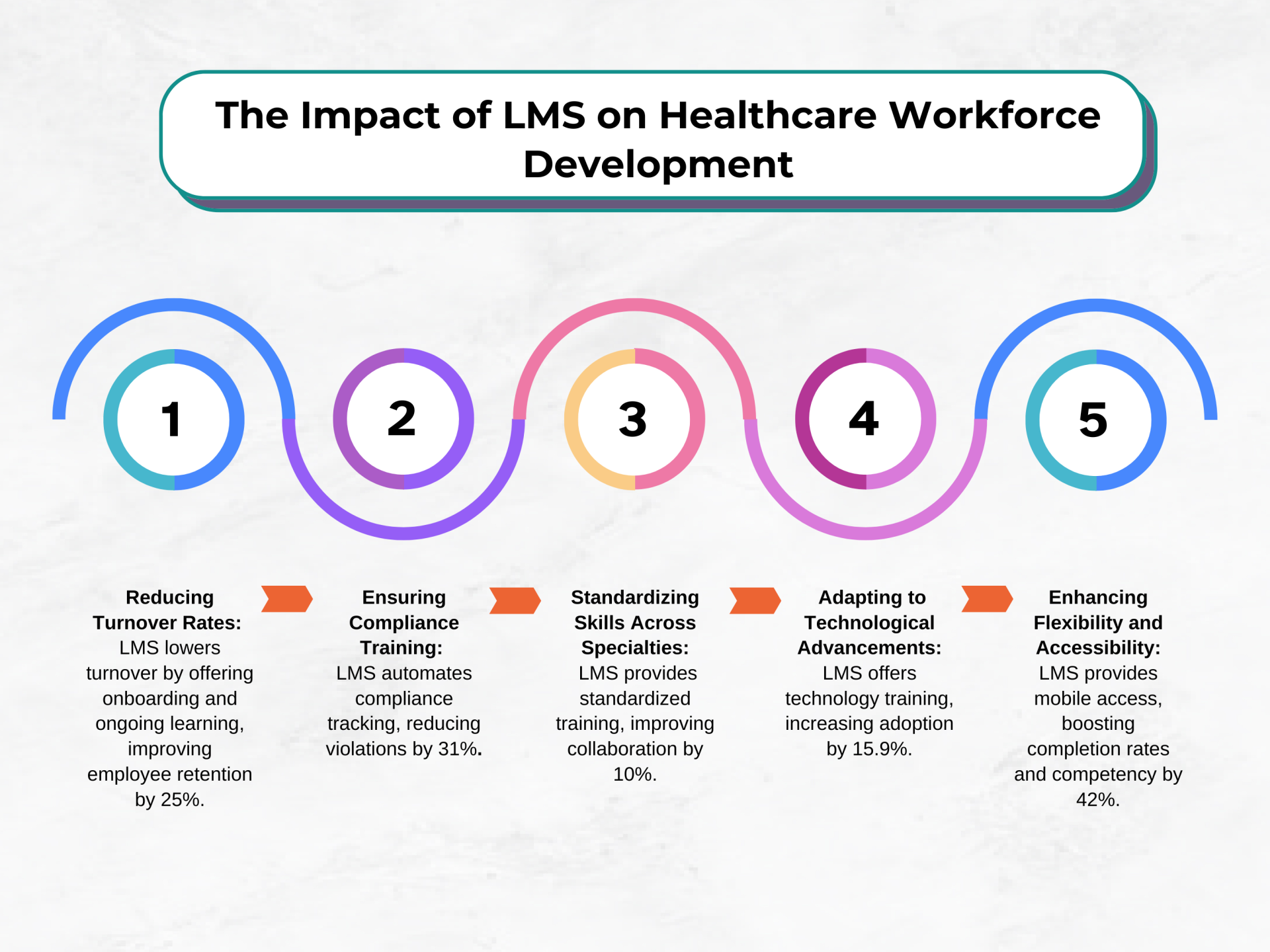
Exploring Key Features of LMS for Healthcare
As the healthcare landscape keeps on developing, the significance of constant schooling and training for healthcare experts couldn’t possibly be more significant. Because of the novel challenges faced by the healthcare area, Learning Management Systems (LMS) tailored explicitly for healthcare have arisen as irreplaceable instruments for working with productive and viable learning and development drives. In this conversation, we will investigate the vital elements of the best LMS for healthcare and their job in changing schooling and training inside the healthcare industry.
1. Customized Content Management
Firstly, LMS for Healthcare offers robust content management capabilities, allowing organizations to create, upload, and organize customized training materials tailored to the specific needs and requirements of healthcare professionals. As per a report by MarketsandMarkets, the worldwide healthcare IT market size is projected to arrive at USD 270.3 billion by 2026, driven by the rising reception of computerized learning solutions like LMS in the healthcare area.
2. Compliance Tracking and Reporting
Also, One of the trademark highlights of LMS for Healthcare is its capacity to track and cover consistency training exercises, guaranteeing that healthcare experts remain in the know regarding administrative prerequisites and accreditations. As indicated by a concentrate via Training Industry, Inc. Software development outsourcing services using LMS platforms report an average increase in compliance training completion rates by 50%, demonstrating the effectiveness of LMS in promoting regulatory compliance.
3. Interactivity and Engagement Tools
LMS for Healthcare integrates intuitive and connecting with learning devices, for example, tests, recreations, and gamification components to improve student commitment and maintenance. Research published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (JMIR) indicates that gamified e-learning interventions result in higher levels of engagement and knowledge retention among healthcare professionals compared to traditional training methods.
4. Mobile Accessibility and On-the-Go Learning
With the mobile accessibility, LMS for Healthcare offers portable openness, empowering healthcare experts to get training materials whenever, anyplace, and on any gadget. As per a review by Brandon Hall Group, 82% of custom software development services USA believe versatile learning to be a fundamental part of their general learning system, featuring the developing significance of in a hurry learning in the healthcare area.
5. Advanced Analytics and Reporting
LMS for Healthcare gives progressed investigation and detailing capacities, permitting associations to follow student progress, evaluate training adequacy, and distinguish regions for development. A study published in the Journal of Continuing Education in Nursing found that healthcare organizations using LMS platforms with robust analytics capabilities experienced a 30% improvement in training results contrasted with those utilizing traditional training methods.
By utilizing these key highlights, LMS for Healthcare enables healthcare associations to convey extensive, drawing in, and compelling training programs. That upgraded the information, abilities, and skills of their labor force, at last prompting worked on persistent results and healthcare conveyance.
Benefits of Implementing LMS for Healthcare Organizations
The execution of Learning Management Systems (LMS) has arisen as an essential basis for healthcare associations trying to upgrade their training and development endeavors. LMS platforms planned explicitly for the healthcare area offer a scope of advantages that can decidedly influence hierarchical proficiency, worker skill, and eventually, patient consideration results. In this conversation, we will investigate the vital advantages of carrying out LMS for healthcare software development services and their job in driving greatness in healthcare schooling and training.
1. Centralized Training Management
Firstly, LMS for Healthcare gives a unified platform to dealing with all parts of training and development drives, including course creation, conveyance, following, and detailing. According to a survey by Brandon Hall Group, organizations that implement LMS platforms experience a 23% decrease in training organization time, prompting tremendous expense reserve funds and functional efficiencies.
2. Cost-Effectiveness and Scalability
Secondly, By leveraging LMS for Healthcare, associations can essentially diminish the expenses related with traditional study hall based training, for example, travel costs, setting rentals, and written words. Research directed via Training Industry, Inc. found that associations that change from traditional training methods to e-learning solutions like LMS experience a typical expense investment fund of 50-70% per learner.
3. Enhanced Accessibility and Flexibility
LMS for Healthcare offers upgraded openness and adaptability, permitting healthcare experts to get training materials whenever, anyplace, and on any gadget with a web association. According to a report by Ambient Insight, the global mobile learning market size is projected to reach USD 78.5 billion by 2025, driven by the increasing demand for on-the-go learning solutions facilitated by LMS platforms.
4. Improved Compliance and Regulatory Adherence
With work in compliance following and revealing highlights, LMS for Healthcare assists associations with guaranteeing that healthcare experts remain in the know regarding administrative prerequisites and certificates. A study published in the Journal of Healthcare Risk Management found that organizations. Using LMS platforms experienced a 40% reduction in compliance violations and penalties compared to those using traditional training methods.
5. Personalized Learning Paths and Competency Development
LMS for Healthcare permits associations to make customized learning ways in light of individual jobs, obligations, and ability levels, empowering designated skill development and profession movement. As indicated by a report by Docebo, 68% of healthcare associations report that customized learning ways conveyed through LMS platforms fundamentally affect worker execution and occupation fulfillment.
By tackling the force of LMS for Healthcare, associations can open a bunch of advantages that add to the nonstop improvement of their labor force. The conveyance of great patient consideration, and the general outcome of their healthcare mission.
Transform Your Business with Custom LMS for Healthcare. Request a Free Consultation Today!
4 Challenges to Solve in Learning and Development in the Healthcare Sector
Learning and development assume a urgent part in guaranteeing that healthcare experts are outfitted with the most recent information and abilities to convey quality patient consideration. However, the healthcare area faces a few remarkable challenges in such a manner, requiring innovative solutions to defeat them. In this conversation, we will dive into four conspicuous challenges experienced in learning and development inside the healthcare area, alongside detailed clarifications and proposed solutions for each.
1. High Turnover Rates and Staffing Challenges
Firstly, Healthcare learning management system vendors frequently wrestle with high turnover rates and staffing deficiencies, which can upset training drives and prevent the coherence of care.
Solution:
Execute complete on-boarding programs that focus on mentorship and backing for fresh recruits. Use mixed learning draws near, remembering on the web modules and hands-for training, to oblige occupied plans and guarantee reliable ability development. Lay out professional success pathways and boost continuous expert development to encourage representative maintenance.
2. Compliance Training and Regulatory Requirements
Secondly, Healthcare experts should stick to severe administrative principles and go through ordinary compliance training to maintain licensure and authorization.
Solution:
Use Learning Management Systems (LMS) tailored for the healthcare area to concentrate compliance training materials and streamline following and revealing cycles. Carry out intelligent and situation based training modules to upgrade commitment and maintenance of critical compliance data. Give progressing updates and supplemental classes to keep staff informed about advancing guidelines.
3. Skill Standardization Across Diverse Specialities
Healthcare includes a wide cluster of strengths and disciplines, each requiring particular ranges of abilities and information bases. Guaranteeing normalization of abilities across these assorted regions can be challenging.
Solution:
Foster capability systems and normalized educational programs that frame fundamental abilities and skills for different healthcare jobs. Execute broadly educating drives and interdisciplinary recreation activities to advance joint effort and ability move among various fortes. Use capability based appraisals and execution input systems to distinguish regions for development and tailor training intercessions appropriately.
4. Keeping Pace with Technological Advancements
Quick progressions in medical technology require healthcare experts to consistently refresh their abilities and adjust to new apparatuses and systems.
Solution:
Offer continuous technology training programs that draw attention on the utilization of electronic health records (EHRs), telemedicine platforms, clinical gadgets, and other state of the art technologies. Encourage a culture of development and computerized education inside custom software development companies in USA by giving admittance to assets, for example, online classes, studios, and online courses. Team up with industry accomplices and scholarly organizations to keep up to date with arising technologies and integrate them into training educational plans.
By tending to these challenges with proactive and innovative methodologies, healthcare associations can encourage a culture of persistent learning and development. Eventually upgrading patient results and propelling the nature of care conveyance.
Steps to Selecting the Right LMS for Healthcare Organizations
Choosing the right Learning Management System (LMS) for a healthcare association is a critical choice that can essentially influence the viability of training and development drives, representative commitment, and eventually, patient consideration results. With various choices available on the lookout, each offering one of a kind elements and functionalities, it’s fundamental for custom software development companies in USA to take on an essential way to deal with choosing a LMS that lines up with their particular requirements, objectives, and monetary constraints. In this aide, we will frame the key advances associated with choosing the right LMS for healthcare associations. Giving reasonable experiences and contemplations to assist with working with the dynamic cycle.
1. Assess Organizational Needs and Objectives
Firstly, Lead a careful necessities evaluation to recognize the particular training and development prerequisites of your medical billing and coding software solutions. Decide the learning goals, interest group, content sorts, compliance needs, and any special challenges or constraints that should be tended to.
2. Define Selection Criteria and Priorities
Secondly, Lay out clear determination standards and needs founded on the necessities evaluation discoveries. Consider factors, for example, versatility, usability, compliance abilities, portable availability, revealing functionalities, incorporation capacities with existing systems, seller backing, and all out cost of possession.
3. Research and Evaluate LMS Options
Research and order a rundown of potential LMS merchants that have some expertise in healthcare schooling and training. Assess every seller in light of their item includes, industry notoriety, client references, contextual analyses, and estimating models. Demand demos or preliminary admittance to survey the usability and reasonableness of every LMS platform.
4. Engage Stakeholders and Obtain Feedback
Include key partners from different offices, including training, IT, compliance, and clinical tasks, in the choice cycle. Accumulate criticism and bits of knowledge from end-clients, executives, and informed authorities to guarantee that the picked LMS addresses the issues and assumptions for all partners.
5. Consider Integration and Compatibility
Assess the similarity of the LMS with existing systems and technologies utilized inside your healthcare association. Such as electronic health records (EHRs), human resources management systems (HRMS), and telemedicine platforms. Ensure that the LMS can seamlessly integrate with these systems to facilitate data exchange and interoperability.
6. Review Vendor Support and Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Survey the degree of help and administration given by every LMS merchant, including specialized help, training assets, execution help, and continuous maintenance. Survey the seller’s SLAs to comprehend their responsibilities in regards to system uptime, execution, and resolution times for issues or disturbances.
7. Conduct Cost-Benefit Analysis
Play out a complete money saving advantage examination to assess the profit from venture (return on initial capital investment) of every LMS choice. Think about both direct expenses, for example, authorizing charges, execution costs, and progressing membership charges. As well as roundabout expenses, like training time, efficiency misfortunes, and potential compliance gambles.
8. Finalize Selection and Negotiate Contracts
In light of the assessment standards, partner criticism, and money saving advantage examination, finish the choice of the favored LMS vendor. Within the Agile Software Development Life Cycle, while constant improvement and adaptability are center standards, there’s an urgent stage for concluding choice and agreement discussion. After iteratively fostering a software solution through Nimble runs, the venture arrives at a stage where partners survey the constructed highlights. They contrast these highlights with project objectives and decide whether the solution lines up with their requirements. Whenever fulfilled, formal agreements with sellers or interior development groups are arranged. This step hardens the settled upon functionalities and conveyance course of events for the end result, guaranteeing clearness and responsibility prior to concluding the Agile SDLC. Arrange contract terms and estimating to get the most ideal arrangement. Guaranteeing clearness based on permitting conditions, installment plans, reestablishment choices, and any extra services or customization necessities.
9. Plan for Implementation and Rollout
Foster an extensive execution plan that frames the timetable, achievements, obligations, and asset prerequisites for sending the chosen LMS inside your healthcare association. Consider factors, for example, data movement, client training, system customization, and change management methodologies to guarantee a smooth progress.
10. Monitor Performance and Gather Feedback
When the LMS is executed, screen its presentation and assemble input from clients to distinguish any regions for development or advancement. Lead standard audits and appraisals to quantify the viability of the LMS in gathering hierarchical objectives and targets. Making changes on a case by case basis to boost its effect on training results and patient consideration.
By following these means and contemplations, healthcare associations can explore the LMS determination process really. Eventually choosing a solution that lines up with their requirements, improves training and development drives, and adds to the conveyance of top notch patient consideration.
Unlock Your Business Potential with Custom Healthcare Software Solutions. Contact us Today!
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Carrying out a Learning Management System (LMS) inside a healthcare association requires cautious preparation, coordination, and execution to guarantee effective reception and reconciliation into existing work processes. While the advantages of LMS for healthcare schooling and training are significant, successful execution techniques and best practices are fundamental. To expand the system’s effect on labor force development and patient consideration results. In this aide, we will investigate key execution techniques and best practices for coordinating Healthcare learning management system vendors, giving actionable insights and suggestions to help a smooth and fruitful execution process.
1. Develop a Clear Implementation Plan
Firstly, Establish a complete execution plan that frames the objectives, goals, course of events, achievements, and asset prerequisites for sending the LMS inside the healthcare custom software development services. Relegate jobs and obligations to key partners and lay out correspondence channels to work with coordination and joint effort all through the execution cycle.
2. Conduct Training and Change Management
Secondly, Give thorough training and backing to clients at all levels of the association to guarantee legitimate usage of the LMS. Offer training meetings, studios, and online assets to acquaint clients with the system’s highlights, functionalities, and best practices. Execute change management procedures to address any protection from change and encourage a culture of ceaseless learning and improvement.
3. Customize the LMS to Fit Organizational Needs
Customize the LMS to line up with the particular necessities, work processes, and prerequisites of the healthcare digital transformation companies. Design client jobs and consents, customize the UI, and tailor content libraries to mirror the association’s marking and training needs. Influence customization choices to make an easy to understand and natural learning climate that reverberates with students.
4. Promote User Engagement and Participation
Cultivate client commitment and support by advancing the advantages of the LMS and displaying its effect on proficient development and patient consideration results. Energize dynamic cooperation through intelligent highlights like conversation discussions, cooperative ventures, and distributed learning networks. Perceive and compensate accomplishments to boost proceeded with commitment with the platform.
5. Ensure Data Security and Compliance
Focus on data security and compliance all through the execution interaction to safeguard delicate healthcare data and maintain administrative adherence. Carry out strong safety efforts, for example, encryption, access controls, and normal reviews to shield data honesty and secrecy. Guarantee compliance with significant guidelines like HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH Act to moderate dangers and liabilities.
6. Monitor Performance and Measure Success
Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and measurements to assess the viability of the LMS systems for healthcare execution and measure its effect on training results and hierarchical objectives. Screen client commitment, course fruition rates, ability evaluations, and compliance measurements to distinguish regions for development and track progress over the long haul. Use data examination and detailing devices to produce noteworthy experiences and illuminate dynamic cycles.
7. Iterate and Improve Continuously
Consistently assess and emphasize on the LMS execution in light of client criticism, execution measurements, and changing authoritative necessities. Request input from partners and end-clients to recognize open doors for improvement and advancement. Carry out ordinary updates, highlight upgrades, and system enhancements to guarantee that the LMS remains lined up with developing healthcare patterns and best practices.
By embracing these execution procedures and best practices, healthcare associations can really send and coordinate a LMS into their training and development drives. Driving enhancements in labor force skills, patient consideration quality, and authoritative execution.
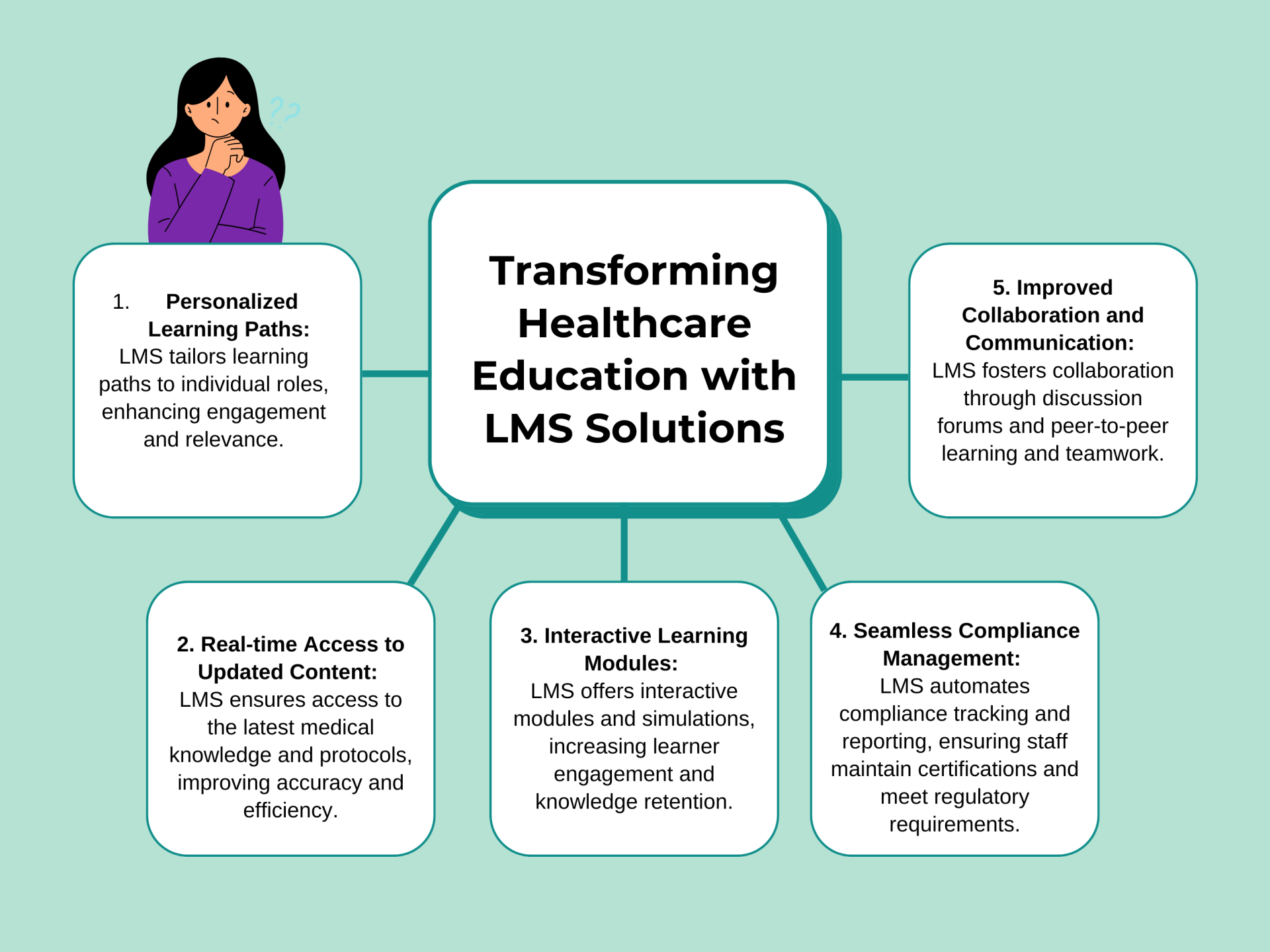
Measuring Success: Key Metrics for Evaluating the Impact of LMS in Healthcare
Estimating the outcome of a Learning Management System (LMS) execution in healthcare goes past following course fulfillment rates or system usage. It includes assessing the effect of the LMS on labor force development, patient consideration results, and authoritative execution. By recognizing key measurements and execution pointers, healthcare associations can survey the viability of their LMS drives and settle on data-driven choices to drive constant improvement. In this aide, we will investigate the vital measurements for assessing the effect of LMS in healthcare and how they add to accomplishing hierarchical objectives and targets.
1. Training Completion Rates
Firstly, Monitor the percentage of experts who effectively complete training modules and courses inside the LMS. High culmination rates demonstrate commitment and compliance with training necessities. While low culmination rates might recommend obstructions to support or inadequate substance.
2. Competency Assessments and Skill Proficiency
Secondly, Direct standard ability evaluations to quantify the information, abilities, and skills gained through LMS training. Track enhancements in expertise capability levels over the long haul to measure the viability of training mediations and distinguish regions for additional development.
3. Compliance and Certification Rates
Measure the level of healthcare experts who maintain compliance with administrative prerequisites and obtain required certificates through healthcare learning management system training. Guarantee that all compulsory training modules are finished on time and that staff individuals remain fully informed regarding applicable guidelines and best practices.
4. User Engagement and Satisfaction
Assess user engagement metrics, for example, login recurrence, meeting length, and support in intuitive exercises inside the LMS. Request input from clients through reviews, center gatherings, and criticism components to survey generally speaking fulfillment with the LMS platform and training content.
5. Time to Competency and Onboarding Efficiency
Track the time it takes for fresh recruits or progressing staff individuals to accomplish skill in their jobs through LMS training. Measure upgrades in onboarding effectiveness and time-to-efficiency to recognize amazing open doors for streamlining processes and improving labor force availability.
6. Patient Care Outcomes and Quality Indicators
Evaluate the effect of LMS training on persistent consideration results and quality markers, for example, patient fulfillment scores, clinical results, drug blunder rates, and disease control measures. Relate upgrades in staff abilities and execution with positive changes in persistent consideration measurements.
7. Cost Savings and Return on Investment (ROI)
Compute the expense investment funds and return for money invested created by LMS execution through variables, for example, diminished training costs, expanded staff efficiency, diminished turnover rates, and worked on tolerant results. Think about the monetary advantages of LMS training with the speculation expected to execute and maintain the system.
8. Compliance Audit Findings and Risk Reduction
Break down compliance review discoveries and chance appraisal data to distinguish patterns, examples, and areas of resistance that might require designated training intercessions. Measure the viability of LMS training in relieving compliance chances and further developing in general hierarchical compliance act.
9. Employee Performance and Development Plans
Survey representative execution assessments and development intends to evaluate the effect of LMS for Healthcare training on individual execution and vocation movement. Recognize relationships between training results, ability development, and execution upgrades to illuminate ability management methodologies.
10. Continuous Improvement Initiatives
Screen continuous drives to further develop LMS usefulness, content quality, and client experience in view of criticism from clients and execution examination. Execute iterative changes and upgrades to the LMS platform to address distinguished regions for development and advance training results over the long haul.
By focusing on these vital measurements for assessing the effect of LMS in healthcare, healthcare software development companies in USA can gain significant experiences into the viability of their training programs, drive persistent improvement endeavors, and at last, upgrade the nature of patient consideration conveyance.
Transform Your Healthcare Software Vision into Reality – Book A 30 Minutes Free Consultation!
Conclusion: Transforming Healthcare Education with LMS Solutions
The adoption of Learning Management Systems (LMS) in healthcare addresses a groundbreaking change in how schooling and training are conveyed and overseen inside the industry. By utilizing LMS solutions tailored explicitly for healthcare associations, foundations can address the extraordinary challenges they face in training and fostering their labor force, at last prompting further developed patient consideration results and hierarchical execution. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global healthcare education solutions market size is projected to reach USD 15.8 billion by 2025. Driven by the increasing demand for continuous education among healthcare professionals.
At last, by carrying out LMS solutions, healthcare associations can understand a scope of advantages, including concentrated training management, cost-viability, upgraded openness, further developed compliance, customized learning ways, and skill development. These advantages add to the nonstop improvement of labor force capabilities. The conveyance of great patient consideration, and the general progress of healthcare associations.
As the healthcare industry keeps on advancing, LMS solutions will assume an undeniably fundamental part in supporting the continuous training and development of healthcare experts. Guaranteeing they remain furnished with the information and abilities expected to satisfy the needs of present day healthcare conveyance. Through essential execution and progressing assessment, LMS solutions have the potential. To drive significant change in healthcare schooling, at last helping patients, suppliers, and custom software development outsourcing companies.
FAQs: Addressing Common Concerns and Queries about LMS for Healthcare
1. How can an LMS benefit our healthcare organization?
A LMS can help your healthcare association in more ways than one. It brings together training management, upgrades openness and adaptability for students. It guarantees compliance with administrative prerequisites, and supports. That customized learning ways tailored to individual jobs and abilities. Eventually, it further develops labor force capability, patient consideration results, and hierarchical effectiveness.
2. Is implementing an LMS cost-effective for healthcare organizations?
Yes, implementing an LMS can be cost-effective for healthcare organizations in the long run. While there might be introductory speculation costs related with software permitting, execution, and training. LMS platforms ordinarily lead to tremendous expense reserve funds contrasted with traditional homeroom based training methods. Decreased costs on movement, setting rentals, and written words, alongside expanded efficiency and compliance. That add to the general expense adequacy of LMS execution.
3. How can we ensure data security and compliance when using an LMS?
LMS vendors focus on data security and compliance with industry guidelines like HIPAA, GDPR, and HITECH Act. They execute strong safety efforts, for example, encryption, access controls, customary reviews. Compliance following highlights to safeguard delicate healthcare data. Moreover, healthcare associations can lay out inner approaches and methods. To guarantee data security and compliance with administrative necessities while utilizing a LMS.
4. What type of support and training are available for LMS users?
LMS vendors normally offer extensive help and training assets to assist clients with expanding the advantages of the platform. This might incorporate onboarding meetings, client guides, video instructional exercises, online classes, and day in and day out specialized help services. Moreover, healthcare associations can offer interior training and backing. To guarantee that staff individuals are capable in utilizing the LMS and getting to training materials really.
5. How can we measure the effectiveness of our LMS implementation?
Estimating the viability of a LMS execution includes following key performance indicators (KPIs). For example, training consummation rates, capability appraisals, client commitment measurements, compliance rates, and patient consideration results. By breaking down these measurements over the long run, healthcare associations can survey. The effect of the LMS on labor force development, patient consideration quality, and authoritative performance. Taking into consideration persistent improvement and advancement of training drives.