Table of Contents
Electronic Data Interchange refers to exchanging business information or data electronically between partners or vendors. Before the concept of EDI was introduced, most communication was done on paper, phone calls, or other traditional modes that are hardly secure or efficient anymore. EDI uses various standards and protocols that guide the processes for executing business transactions and keeping them in compliance. With a compound annual growth rate of 12.5%, the size of the global market for Electronic Data Interchange software is expected to increase from $1.98 billion in 2023 to $4.52 billion by 2030.
Contrary to assumptions, EDI is quite an old concept. Marking its existence since the 1970s when it was inspired by military logistics. Amongst various aspects of EDI solutions, EDI mapping is the most common and popular one. However, many companies are still not familiar with its importance and role in making their business transactions successful.
As per Michael Lee, an EDI consultant-“Clear communication is the foundation of successful EDI implementation. Understanding your partner’s needs and expectations is key to establishing accurate mappings“.
An Overview of EDI Mapping
EDI mapping refers to the process through which EDI data is translated into a much simpler format that is easily used in new environments. It is the translation of data structures from a proprietary file, such as in CSV format, SAP Idiocy, txt, ERP-specific, etc., to a standard format that includes EDIFACT, ANSI X12 EDI Standards, and more. In simple words, you can say that EDI mapping describes how to convert information into two unique formats – a company-specific data format and a standardized industry-wide EDI format.
On one hand, the corporate ERP solutions integrate data automatically while on the other, a standard-based format is sent to trading partners that use EDI and the same formats. It allows you to generate conversion programs from the description. With an EDI provider to assist you, all the outbound processing converts the file formats to EDI that can further be shared with partners. The inbound processing translates the EDI format into an in-house file format.
So, you can sum it up in three basic steps-
- Preparing the documents
- Transfer them into EDI formats
- Transmit the EDI files to partners
Steps for Mapping Factory
Electronic Data Interchange is the exchange of business documents in a specific standard format. It is an operational procedure for most businesses in the exchange of data. It has been making the process much more efficient and streamlined. However, mapping is a complex and at times very difficult process for companies. Especially for the ones that are new to the technology.
Mastering EDI Mapping- 6 Point Steps
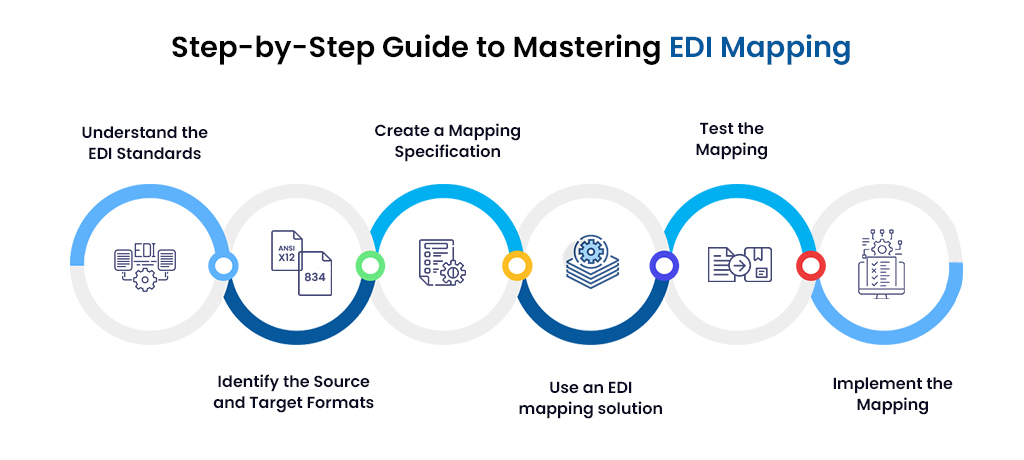
Step 1: Understand the EDI Standards
If you want to master EDI mapping, you must know what the EDI standards are. A few of the EDI standards include ANSI X12, EDIFACT, and TRADACOMS. These standards define the structure and format of the data. Understanding the EDI standards is critical to developing an accurate mapping specification.
Step 2: Identify the Source and Target Formats
The next step is identifying the source and target formats. The source format is the data format with which the trading partner is exchanging. In contrast to the target format, which is the format in which data needs to be transformed to be compatible with the EDI system of the recipient. Knowing the source and target formats is critical for coming up with an accurate mapping specification.
Step 3: Create a Mapping Specification
Once you have identified the source and target formats, creating a mapping specification is next. A mapping specification is a document that defines how the data will be transformed. Specifically from the source format to the target format. It should include the following information:
- The source and target formats
- Mapping rules for each data element
- Data transformation rules
- The validation rules
- The error-handling rules
Step 4: Use an EDI mapping solution
EDI mapping can be a time-consuming and challenging process. However, a mapping solution can make the process easier and more efficient. The solution provides pre-built maps for everyday transactions and can help automate the mapping process. They also offer validation and error-handling features that can help ensure the accuracy of the data being exchanged.
Step 5: Test the Mapping
Testing the mapping is an essential step in the EDI mapping process. It is critical to ensure the accuracy of the mapping specification before exchanging data with trading partners. Testing the mapping involves verifying that the data is transformed accurately from the source to the target format. It also involves testing the validation and error-handling rules to ensure they function correctly.
Step 6: Implement the Mapping
Once the mapping has been tested and validated, it is ready for implementation. Implementing the mapping involves configuring the EDI system to use the mapping specification for exchanging data with trading partners. Ensuring that the mapping is implemented correctly is critical to avoid any data exchange errors.
.
Once the mapping has been tested and validated, it is ready for implementation. Implementing the mapping involves configuring the EDI system to use the mapping specification for exchanging data with trading partners. Ensuring that the mapping is implemented correctly is critical to avoid any data exchange errors.
.
Monitoring and Maintenance is also a crucial step since the EDI standards keep on changing. As per a specialist in EDI, John Smith” The biggest challenge with EDI mapping is dealing with the complex and ever-changing nature of EDI standards and partner requirements“
Reduce EDI Mapping costs and Errors
The Need for EDI Mapping
In EDI, when the concern is primarily the exchange of data and information, mapping is required to assign the data source and destination correctly, i.e., sender and recipient. It transforms internal formats into standardized and uniform message formats and vice-versa. The EDI mapping has specific instructions for the same. Hence, it represents proprietary customer interface data exchange settings with each partner along with a standardized data exchange procedure. This enables EDI traffic to run smoother without any specific programming.
Mapping is similar across various industries but there can be a difference in fields and documents. For retail and e-commerce solutions, EDI documents can be completely different from finance or supply chain. For some businesses, tracking orders can be critical while for others, it may hardly matter. Therefore, the important thing is the ability to manage data in mapping that is not accommodated in a particular ERP.
Supplier Side
Two orders received by a supplier for the same goods or products may be completely different. Every case or pack maintained by customers must translate to the units used by the supplier. Mapping is done to maintain cross-references, such as ship-to-address code, distribution center number, buyer’s ID, etc.
Buyer Side
The buyer side of the map must accommodate all the fields used by a customer. This is done by EDI software or EDI mapping service providers. They refer to fields used by a customer as a universal map that has two sides. The most complex part is connecting the other end to the supplier’s ERP. The mapping parameters are managed through application software, cloud-based EDI, ERP tables, mapping software modules, and custom programming. As handling user-specific logic is common, standardized capabilities that can maintain version-to-version ERP compatibility are the best.
Cloud Based Approach
The cloud-based approach to hybrid EDI offers unparalleled visibility by ensuring that you can standardize information flows. Moreover, with hybrid EDI solutions, traders can –
- Smoothen entire process
- Empower themselves with the ability to adapt and accommodate
- Make communications easier
- Simplify onboarding process
Translation Basis for the EDI Converter
EDI mapping connects the source and target fields of the two different formats and provides the work instructions for the converter. With EDI conversion software, data is converted into an in-house system (source) into a standard format, such as XML. EDIFACT EDI, CSV, flat file, X12. The converter writes incoming data in this format to interfaces at the receiver as the target. He will seek all instructions and specifications required to create new files in the desired standard format. With EDI mapping, you also get a high degree of flexibility. For example, for customer-specific mapping, you can respond to partners’ change requests instantly and easily with extensive expertise in EDI tools and programming.
Advantages of EDI Mapping

EDI mapping enables a business to translate data between different EDI formats and systems. We shall now see what the benefits of EDI mapping are.
Efficient Data Exchange
EDI Mapping supports the efficient data exchange of a business with its trading partners through data translation between different EDI formats or systems. It ascertains that the data is accurately delivered and in the right format, thus saving from errors and additional work. EDI Mapping enables organizations to run a much smoother way of data exchange and thus facilitates the efficiency of their supply chain operations.
Improved Communication
Proper communication is essential for the effective operation of a supply chain. EDI mapping solutions enable companies to communicate effectively with their trading partners by offering the translation of data from one format into a different format and another computer system. This ensures that information is availed to every party, hence reducing possible risks of miscommunication and promoting clear communication.
Fewer Errors
EDI mapping solutions guarantee the high accuracy of the information exchanged between trading partners. Translating data from one format and system into another, EDI mapping solutions can help reduce the risks of errors and discrepancies in data exchange. It helps in improving the quality of data and makes certain that all parties have access to accurate information that will be up-to-date.
Improved Productivity
EDI mapping aids productivity in that it automates the processes involved in data interchange, thereby reducing manual data entry. The EDI mapping solutions help a business smooth the supply chain operations by spending less time and less manpower on exchanging data with the trading partner. It enables businesses to put more effort into other critical areas of the operation, such as product development and customer service.
Enhanced Visibility
EDI mapping solutions give businesses greater transparency over supply chain operations since they know how goods and information are moving at any time. As a result, they are better placed to trace problems or bottlenecks that may exist within their supply chain and take corrective steps before they spiral into serious issues. With improved visibility, a business can make more knowledge-driven decisions that will better improve the overall performance of their supply chain operations.
Cost Savings
EDI-mapping solutions can help companies save money in a variety of ways, such as by reducing manual data entry and increasing supply chain efficiency. Businesses will spend less time and effort exchanging data with trading partners; hence, this reduces labor costs, improving productivity. Besides, EDI mapping solutions identify inefficiency notes within any business’s supply chain operations, after which the owner can take corrective action to reduce costs.
Compliance with Regulations
EDIM solutions can provide compliance with industry regulations and standards such as HIPAA and ASC X12. Besides translating data between EDI formats and systems, the EDI mapping solutions can also ensure a firm’s compliance with provisions in the regulatory setup of the country for exchanging data. This ensures that a business is protected from expensive penalties, fines, and other reputational damage within the marketplace.
Integration with ERP Systems
EDI mapping solutions can be integrated with Enterprise Resource Planning systems, thereby enabling any business to automate their data exchange process for better efficiency in their supply chain. Companies can integrate EDI data into their ERP systems with the help of EDI mapping solutions for easy management of their supply chain operations.
Hiring an EDI solution provider can help build XML formats used by businesses or trading partners while retaining the investment in EDI infrastructure. The first and original form of EDI mapping used customized in-house software that links EDI and in-house ERP or accounting systems. However, this was quite an expensive and complex process. Companies adopted it on a large scale to eliminate manual data entry tasks in the back-end systems.
Are You Prepared to Become an Expert in EDI Mapping? Get Started on Your Trip Right Now!
Challenges in EDI Mapping
Complexity:
One of the most critical challenges for EDI mapping is the complexity of the process. EDI mapping is a process that requires a conversion from one format to another; this could get very complex and time-consuming. It needs a great deal of knowledge about source and target data formats at a deep level, along with programming languages and data mapping tools.
Compliance:
One of the most critical challenges for EDI mapping is the complexity of the process. EDI mapping is a process that requires a conversion from one format to another; this could get very complex and time-consuming. It needs a great deal of knowledge about source and target data formats at a deep level, along with programming languages and data mapping tools.
Data validation
This is another big challenge for EDI mapping. Since EDI involves data transfer in huge amounts across multiple systems, the data must be accurate, consistent, and valid. Validation of data may take time, and any inconsistencies or errors in them might delay and cause errors when processing is done.
Ensuring data security
Yet another critical challenge in EDI mapping is data security. It deals with the process of exchanging sensitive data, like financial information. This is why it becomes very important that the data is secure or protected from any unauthorized access. Robust security measures in terms of encryption, authentication, and access control have to be in place while developing EDI mapping solutions to avoid data breaches and ensure data security.
EDI services can, therefore, help companies surmount these difficulties by facilitating data exchange. Mapping solutions provide a wide array of features and functionalities, including data mapping, transformation, validation, security, and so on. They may further be combined with other EDI solutions like EDI translators and VANs to provide an end-to-end EDI solution.
Best Practices for EDI Mapping
EDI mapping creation involves building interface files for translating the files from one form to another. These files are made to support both ERP apps and any EDI transaction for trading partners to exchange data securely.
However, the type of files used in these transactions depends on the type of business niche and requirement as well as how a business wants to process the data with their ERP.
The key aspect of creating EDI interface files is standardizing in-house naming conventions that can comply with all other files. Because EDI implementation can be affected by external and custom programming that is designed for interfacing.
Standardizing files can help users identify their purpose and keep them organized. Hence, when developing the files, these items should be considered-
- Direction Code-In, Out, Send, Receive
- Map/Transaction Type – 810, 277, 834, INV, PO
- Structured Data Levels – Header, Detail, Address, Note
- Segment Labels – BEG, IT1, N1, MSG
- Element Labels – BEG01, IT102, N104
The column names, the Element ID, and Elements Description details must also be added to help future technicians identify the purpose of the EDI file. Hence, it is always recommended to add complete information to each transaction file to simplify file transfer. For instance –
Field Name can be added “CSTORD” which describes customer order. The Description field can be explained as “Cust Ord#” which makes any trading partner understand the file element.
Moreover, users can also make customized changes by adding new objects to underline the field type.
Direct EDI Mapping Versus Indirect EDI Mapping
Direct EDI mapping is also referred to as 1:1 Mapping. The term 1:1 Mapping is also stated as 1:1 translation. The reason behind this reference is single mapping creation. Yes, to transfer the information from the source structure to the target structure, only one mapping is created between the trading partners in a direct mapping.
Indirect or Canonical EDI Mapping
On the other hand, Canonical or Indirect Mapping simplifies complex transactions. With Indirect mapping, users can seamlessly maintain mapping and change management with EDI messages or formats at any point in time.
Canonical Mapping offers partner mapping with a standardized format that is specific for each trader. With Indirect mapping, users can quickly convert the EDI messages into abstract layer format to suit their systems. This format can be further converted into an in-house format, which can be consumed by the ERP system easily and used later.
This form of EDI mapping makes EDI format conversion much easier, faster, flexible, and scalable.
We Can Simplify Your EDI Mapping
Selecting the Right EDI Software
While choosing the most reliable software solutions for EDI, make sure to consider the following questions:
1. Do I have skilled people in the organization who can use EDI software?
Let’s face it – not everyone can know how to use EDI mapping software and make the best of it. You need proficient and experienced employees who are adept at EDI and its components. So, do you have people with relevant skills who can use this software? If not, it’s better to connect with a professional EDI-managed services provider who can perform all your tasks and recommend the right solutions.
2. Is the EDI mapping software flexible?
Of course, your business will grow and develop, and so should your EDI infrastructure and system. Thus, the software you select must be flexible and scalable according to your business needs. It must be easy to upgrade as your operations expand, easy to use, and meet your requirements.
3. How much does an EDI mapping software cost?
Budget is a primary concern for many businesses as they cannot spend extravagant amounts initially. So, it is important to decide on a budget as you start with EDI mapping software. It might cost you tens of thousands of dollars and setting a few criteria, in the beginning, will ensure that the money is invested in the right direction and reap maximum benefits. Apart from the cost of software, you must include additional services required for implementation and integration.
4. Is your business ready for EDI Mapping?
Just deciding that you must go for EDI software development is not enough. You have to determine if your business is ready for this change. Also, you must have all the necessary information to ensure that the EDI project is successful. Make sure that the system is well-coordinated with your in-house processes for effective results.
Connect with Us
As you now have all the information and knowledge about EDI mapping, we are sure that you are all set to seek help from a professional EDI service provider. Get in touch with A3Logics, our trusted EDI partner with a team of experts available round the clock to assist you and guide you at every step.
Looking for EDI mapping for your business
Call us or drop an email and we will reach you back ASAP with the best solutions to achieve your business objectives.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is EDI mapping in SAP?
EDI mapping in SAP is a process of translating EDI messages into a format understandable by the data structure of SAP. The EDI messages may be of any format and standard; hence, an SAP system would require EDI data to be mapped with specific fields and structures. Mapping EDI fields with SAP data, defining conversion rules, and configuring EDI partner profiles are all constituents of the EDI mapping process to ensure that EDI data is correctly processed in an SAP system.
EDI mapping within SAP can become very complex. Such specific knowledge about the EDI standards and formats in use, as well as SAP data structures and business processes, is called for. EDI mapping, if implemented correctly, will help streamline business operations, decrease errors, and make them more efficient. This is accomplished by the automated exchange of key business documents between trade partners.
How do you map EDI data?
EDI data mapping is a process for translating EDI messages into a format that the destination system can understand. This involves several steps: identifying source and target data structures, specifying appropriate mapping rules, and validation.
You will be able to map EDI data either by using specialized EDI mapping software or through services that offer graphical design and test environments for EDI mappings. These tools normally support a range of EDI standards and formats and enable you to set up EDI field-target data field mappings graphically, implement mapping rules via drag-and-drop interfaces, and test the results for validity using test and debug tools. Alternatively, you can code custom implementation rules of EDI mapping in a scripting language like XSLT or Java. That would involve more advanced technical knowledge but support very sophisticated flexibility and a much better grade of customization.
How to parse EDI files?
Parsing an EDI file means to extract and process the data contained in the EDI message. Structuring of EDI files uses specific segment, element, and sub-element delimiters. Parsing means breaking up an EDI message into its segments, elements, and sub-elements.
There are a lot of tools that read EDI files. You can, however, outsource to a parser capable of handling several EDI standards and formats by using dedicated EDI parsing software or services.
Normally, such tools provide prebuilt parsers that would fast-track the extraction of data from the EDI message while providing validation features and error checking. Custom parsing scripts can also be created with the help of scripting languages like Python or Java. It requires more technical expertise and allows more room for flexibility and customization.
What are the two EDI file types?
There are two major EDI files: EDI interchange files and EDI transaction files.
The EDI interchange files are used to exchange EDI messages among trading partners. Generally, they contain several EDI transactions that have been grouped. An EDI interchange file is headed by an interchange header segment identifying the sender and the receiver of the interchange and ended by an interchange trailer segment.
In contrast, EDI transaction files hold only one EDI transaction and are helpful in internal processing within the companies’ systems. An EDI transaction file shall include a transaction header segment, one or more data segments, and a transaction trailer segment. The transaction set may include purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices.
The two types of EDI files also follow certain formatting rules and standards like ANSI X12, EDIFACT, or TRADACOMS.
How does EDI mapping work?
EDI mapping transforms data from one format to another, so data is easily transferred between distinct systems. Mapping involves a series of steps:
- Identification of source and target data structure,
- Mapping of EDI fields to target data fields,
- Defining conversion rules
The common starting point in the EDI mapping process is to generate an EDI partner profile, which defines the exact EDI format and version the trading partner is using, along with the mapping rules to convert data into the target format.
Following this, parsing of EDI messages is done for extraction of the data segments, elements, and sub-elements. It then has to be mapped to the equivalent fields in the target system, say, for example, in SAP. Mapping essentially involves the identification of the data elements from the EDI message and matching them to the corresponding fields in the target system.






