Table of Contents
When thinking of a private health insurance exchange, you just think of a marketplace full of options. But that’s not it! There is a lot of work that goes into health insurance exchanges. Enrolling the files, member maintenance files, plan data, billing data, and rating data and much more. Electronic Data Interchange is a key component for exchanging data. Especially because the healthcare industry heavily relies on EDI. In 2023, the size of the healthcare electronic data interchange market was estimated to be USD 4.98 billion. The industry for global healthcare electronic data interchange is expected to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.36% between 2024 and 2032, from USD 5.43 billion in 2024 to USD 11.11 billion. Understanding how EDI 834 transactions work can help businesses streamline their operations and improve communication with their partners and clients. As per the statement by Dr. William Brown, “EDI 834 transactions are the backbone of accurate and efficient health plan enrollment in the US healthcare system. They ensure seamless exchange of patient data between providers and payers“
Role of EDI 834 Transactions
EDI 834 transactions play a crucial role in facilitating the transfer of enrollment and maintenance information. This information includes details about the payer, sponsor, and members involved in offering benefits products. From insurance agencies and government bodies to unions and employers, EDI 834 transactions are widely useful for the employee benefits administration process.
In this article, we will delve into the history of EDI 834 transactions and the standard way to exchange enrollment data via ASC and HIPAA 834 – Benefit Enrollment and Maintenance File format. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a benefits administrator, or simply curious about the subject, this guide will provide valuable insights and information on 834 EDI transactions.
Get Ready for a Seamless Open Enrollment Process!
Contact A3Logics Today and get your benefits enrollment hassle-free
Brief History of EDI 834
EDI 834 was introduced in the 1990s. It was part of a broader push to transform healthcare administrative processes using electronic data interchange (EDI). Paper-based healthcare transactions slowed down the system, so industry groups worked with the federal government to establish EDI standards. The 834 EDI transaction set was created to electronically transmit payment information for health insurance claims. The goal was to reduce costs and errors. This could be done by automating the important but time-consuming administrative process.
The EDI 834 standard was defined by the Health Care Administrative Simplification Compliance Act of 1998 and subsequently added to the HIPAA legislation. Shortly after that, 834 files became widely adopted as major health insurers and providers began to implement EDI systems. Today, the vast majority of health insurance claim payment processing happens using 834 files improving efficiency and reducing costs for both providers and insurers.
What is the EDI 834 file and transaction set?
The EDI 834 file comes in handy for the transfer of health care insurance claim payment information. This is transferred electronically between insurance companies and health care providers. The EDI 834 transaction set consists of payment information about claims to providers from insurance companies.
This includes individual claim data such as patient information, claim number, total amount paid, adjustment amounts, and remittance advice. These files are used by providers to record payments accurately in their accounting systems. Also, these files simplify and automate the procedures of payment recording for providers. Again, the use of the 834 EDI instead of generating paper checks and explanation of benefits reduces administrative costs for insurance companies and health providers alike.
Defining EDI Benefit Enrollment and Maintenance
EDI 834, the transaction set that represents the benefits enrollment and maintenance information. This transaction set shall be used by employers, government agencies, enrolling members, insurance agencies, union agencies, and others included in the healthcare benefits plan to enroll members in a sponsored benefits program or to maintain a member’s current enrollment. Based on HIPAA, some administrative procedures are required to utilize standardized electronic transactions.
Parties
EDI 834 establishes seamless communication between the sponsor of an insurance product and the payer. To put it otherwise, the sponsor is an entity paying for a benefits plan, and the product of insurance, which is the payer—insurer, administers it.
In other words, a sponsor is the party responsible for paying for the benefit plan, while the insurance company itself pays—a benefactor. The 834 transaction set is one of the most largely adopted transactions in health care; it encompasses a very important part of the enrollment process about benefits. It is utilized in different ways by various stakeholders due to their different needs and goals. Health plans make use of EDI 834 in handling enrollment and maintenance data for their policyholders, while employers utilize it in transmitting the health plans’ benefit and open enrollment information to their workers.
EDI 834 for TPAs
Third-party administrators also take advantage of the EDI 834. They use it to handle the enrollment process for several customers, including employers and health plans. Agencies such as Medicare utilize it to process enrollment information for those who are eligible. Furthermore, EDI 834 services providers that offer open enrollment solutions frequently use the EDI to exchange data with both health plans and employers. In essence, the EDI 834 transaction set is an indispensable tool that guarantees an efficient and precise benefits enrollment process in the healthcare industry.
Uses of EDI 834
Not to mention, the EDI 834 file format was specified by the HIPAA 5010 standard for electronic exchange. Other than new enrollments and plan subscriptions, 834 transactions may be used for –
- Changes in any member’s enrollment.
- Reinstating a member’s benefits enrollment.
- Disenrollment of any member (termination of plan membership).
The 834 EDI is organized into segments and data elements, where data elements contain a data field while the segment contains one data element.
Within a data element, you will find
- The date of the transaction,
- Type of insurance plan,
- Premium amount,
- Coverage details
How is EDI 834 Processed and Used?
834 files in healthcare are electronically transmitted over an EDI network. From a health insurance company to a healthcare provider. When the insurance company has processed claims submitted by healthcare providers, it prepares the EDI 834 comprised of information regarding claim payments. The EDI 834 file will be transmitted to the respective providers via the EDI network. Major EDI service providers provide secure connections and software to healthcare organizations to download, process, and upload EDI 834 files.
The electronic data interchange providers then import the EDI 834 files into the billing systems using EDI processing software. This in turn automates the posting of payments into the system. The 834 EDI files also contain information that allows the software to then match each payment to the proper claim and patient’s account. It updates the EDI 834 file import in the provider’s billing system, correctly applying those changes to the patient’s balance. This is an automated alternative to receiving paper checks and explanations of benefits Fairfax, searching for claims, and applying for payments.
Key Advantages of EDI 834
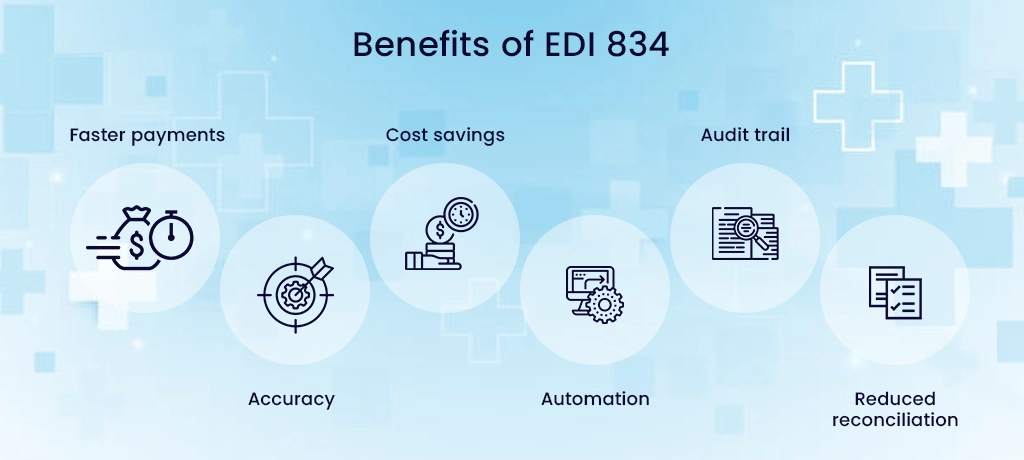
- Faster payments: EDI 834 can be transmitted and processed automatically, allowing providers to record payments faster than paper checks. As a result, it improves cash flow.
- Accuracy: 834 EDI contains standard data elements that map accurately to provider billing systems, reducing payment posting errors.
- Cost savings: These files eliminate the costs of processing paper checks and explanations of benefits, saving money for insurers and healthcare providers. EDI service providers in the USA help realize these cost savings.
- Automation: 834 files automate the payment recording process for edi solution providers, reducing manual labor and data entry.
- Audit trail: The 834 EDI contains a detailed transaction history that provides an electronic audit trail for payments.
- Reduced reconciliation: EDI 834 provides all the payment details needed for automated payment posting and reconciliation with minimal manual effort.
EDI 834 Specifications and Implementation Format
The EDI 834 file has a specific data format or specification that healthcare EDI transactions follow so that different organizations can exchange payment information electronically. The most common 834 implementation format is ANSI X12. EDI service providers in the USA help healthcare organizations set up and send EDI 834 files that follow the ANSI X12 EDI 834 specification. Below is the format defined and used by most EDI-managed service providers.
EDI File Format
ISA’01*0000000000-01-0000000000*ZZ ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOʻZZ*123456789012345 101127*1719*U*00400*000003438*0*P”>
GS’PO-4405197800*999999999-20101127*1719-1421*X*00401OVICS
ST*834*0179
BGN*00*1*20050315 110650****4
REF*38 SAMPLE_POLICY_NUMBER
DTP’303 D820080321
N1 P5 COMPAN_NAME FI”000000000
INS’Y*18*030-20-A
REF’OF’SUBSCRIBER NUMBER
NM1’IL 1 JOHN DOE’R”*34*1’0000000
PER’IPHP 2138051111
N3’123 SAMPLE RD
N4’CITY’ST 12345
DMG D8 19690101 F
HD-030
DTP 348’D8’20080101
REF 1L’INDIV_POLICY_NO
SE 160179
GE 11421
IEA*1’000003438
Creating a benefits enrollment can be done manually into the standard EDI document or pulling out information from data B2B EDI integration from the in-house managed providers.
With automated EDI, creating and sending the information becomes even faster. The EDI translator converts the data received into 834 documents while meeting the strict guidelines set by ANSI X12 EDI standards.
Healthcare EDI Solutions
A flexible and modern EDI supports all EDI communications methods for the payer and the receiver to seamlessly share valuable data with absolute security despite changing industry standards and trends. As EDI has accelerated and been adopted, most EDI providers use advanced solutions to communicate or transmit data, like –
- Cloud-based EDI
- On-premise EDI
- Hosted EDI
- Off-premise EDI
- Strategy Consultation
- HIPAA Compliance
- EDI Assessment
- Process Automation
- EDI Van Services
Start leveraging the power of EDI 834 transactions to improve your business operations.
Components of EDI 834 transactions
An EDI 834 contains several important components that make up the claim payment information transmitted between a health insurer and a healthcare provider. Top EDI providers help clients generate standardized 834 files for healthcare EDI transactions.
The key components of an EDI 834 file are:
- Header information: This includes sender ID, receiver ID, transaction set control number, and date to identify the file and trading partners. It provides a reference for the entire transaction.
- Payment information: This details the actual claim payments, including the patient control number, payment amount, date of payment, payment number, and payment reference codes. It specifies which claims the payment covers.
- Adjustment information: Any adjustments to claim payments are specified here with adjustment reason codes and corresponding positive or negative adjustment amounts.
- Remittance information: This contains information that healthcare providers need to post payments accurately. It includes check numbers for paper payments, electronic funds transfer details, or payment allocation by the claim.
- Acknowledgment information: An optional component where the receiver can send an EDI 997 ACK file to acknowledge receipt of an EDI 834 transaction.
- Trailer information: Contains counts of the various segments in the file to verify completeness and accuracy.
Together, these components make up a complete and standardized EDI 834 file that allows insurers to electronically transmit accurate claim payment information to providers. EDI 834 in proper format ensures that payments are recorded into provider billing systems automatically. As a result, it improved the efficiency of the payment process and reduced administrative costs for both parties.
Common 834 segments include:
- INS: Insurance Information Segment
- DTP: Date or Time or Period Segment
- NM1: Individual or Organizational Name Segment
- REF: Reference Information Segment
- PER: Administrative Communications Contact Segment
- AMT: Monetary Amount Segment
- HD: Health Coverage Dates Segment
Finally, the data elements within an 834 file must be organized correctly to ensure that they can be read and processed by the recipient. The file is structured according to the ANSI X12 format, which specifies how data should be formatted and arranged. The X12 format ensures that data can be transmitted between different systems and applications without errors.
Steps to set up EDI 834 transactions
Setting up 834 transactions requires careful planning and coordination between trading partners. The key steps involved are:
- Identify the scope of the project:
Details to be transferred, structure, and trading partners are some of the features that identify the scope of a project.
- Choose EDI software:
You’ll definitely be in search of an EDI software solution that can let you translate business data into the required format for EDI. Select EDI software that will give you a lot of integration to the already running systems in your company, yet offer all the functionalities to carry on with your EDI transactions.
- Establish communication protocols:
It will be time to determine how you are going to exchange your EDI files with your business partners. You may use a value-added network (VAN), direct EDI communication, or even a web-based portal.
- Set up trading partner agreements:
Setting up trading partner agreements with any of your trading partners will outline the terms for EDI transactions. This shall include identifying data requirements, communication protocols, and security measures.
- Map EDI data to internal systems:
This involves taking EDI data and mapping it into your own internal systems in order to process the data correctly. It basically is a step which identifies every data element in the EDI file with application data and then maps it with the right field in the internal systems.
- Test the EDI implementation:
Test the EDI implementation with your trading partners to make sure that the data is being correctly interchanged. This procedure consists of the exchange of test files and ensuring proper management of data.
- Go live:
Once EDI implementation has been tested you can start interchanging live EDI transactions with your trading partners.
- Monitor and maintain EDI implementation:
Monitoring and maintaining an EDI implementation permits one to be certain of the proper working of the processes involved. This comprises keeping track of transaction volumes, analyzing EDI error reports, and troubleshooting any kinds of problems.
Tips for successful implementation
An implementation may be termed successful if the time for manual processing can be reduced or accuracy improved, or if there is smoothness in communication with trading partners. Well-defined goals will help to keep the process of implementation on track; it also aligns your implementation with your organization’s strategic goals. While selecting an EDI solution, you look at security features and scalability while making sure compatibility with the existing systems in your organization. This may also be helpful to work with a trustworthy EDI Service Provider who has proven success in previous implementations.
Testing and Validation
Thorough testing and validation are essential to ensure that the EDI implementation is working accurately. Planning for testing can involve exchanging test files with trading partners, conducting end-to-end testing, and verifying that data mapping is correct to internal systems.
Communication
Another crucial factor in achieving a successful EDI implementation is establishing unambiguous communication protocols with your trading partners. Clear communication protocols can ensure that everyone understands the requirements and processes involved in EDI transactions. In addition, providing EDI implementation training to employees and trading partners is a must. It can aid in decreasing errors and enhancing the overall efficiency of the implementation.
Monitoring and maintaining
This involves tracking EDI transaction volumes, monitoring error reports, and addressing any issues that arise promptly. Making continual improvements to the implementation can optimize efficiency, enhance accuracy, and decrease costs over time. This can involve analyzing transaction data to identify areas for improvement and making updates to internal systems and processes as needed.
By following these tips, organizations can successfully implement EDI transactions, including EDI 834, and realize the benefits of streamlined benefits enrollment processes.
Best Practices in Implementing EDI 834
There are several best practices to implement EDI 834 files for healthcare organizations successfully. EDI solutions can help smaller providers and businesses exchange EDI 834 , while large insurers may have in-house EDI providers.
- Conduct an assessment of your current payment processes. Identify pain points, costs, and manual efforts to prioritize where EDI 834 can bring the most benefits.
- Choose an EDI provider that understands the healthcare EDI 834 standard and has experience implementing it for other organizations. They can guide you through the entire process.
- Build data mappings between your internal systems and EDI 834 data elements. Test mappings thoroughly to avoid payment posting issues. For insurers, map claims data to generate accurate 834 files. For providers, map EDI 834 data to record payments correctly.
- Establish internal policies for handling and storing 834 files. Designate staff roles and responsibilities for receiving, processing, and troubleshooting EDI 834.
- Set up infrastructure like secure FTP connections, EDI servers, and network firewall rules to exchange EDI 834. Ensure systems are HIPAA compliant.
- Conduct testing with your exchange partners before going live. Simulate end-to-end EDI 834 file transfers and processing to identify and resolve issues.
- Provide training to staff on EDI 834 formats, file transfer, and error resolution processes to ensure smooth transitions to new procedures.
- Monitor EDI 834 volumes, processes, and issues closely after going live. Work with your EDI provider and exchange partners to resolve errors quickly and improve processes over time.
Want Help in Implementing 834 transactions?
Our Experts will Help You
What is HIPAA 834 transaction?
The HIPAA 834 transaction is useful for enrolling individuals into health insurance plans. It makes it easier to notify insurers of changes to an existing enrollment, and terminating coverage. The 834 transaction provides basic information like:
- insured’s name
- date of birth
- address,
- Social Security number
- data on the enrollee’s insurance plan like coverage type, effective dates, and subscriber and member identifiers.
Health insurers, health plans, brokerage firms, employers, and government agencies use the standard 834 formats. They electronically exchange enrollment information to ensure accurate and timely updates to insurance memberships.
What is PHI under HIPAA?
PHI refers to Protected Health Information. According to the HIPAA, PHI refers to any information that we create or receive regarding health. Specifically by a covered health care provider, health plan, employer, or health care clearinghouse. This info can be in relation with past, present, or future and physical or mental condition of an individual. This includes a person’s name, birth date, diagnosis, lab test results, address, and other identifiers.
It is, therefore, mandatory to restrict access to important information regarding patients under HIPAA to protect PHI. The right safeguards placement ensure to prevent improper use or disclosure of information. Other statutory rights available to patients under HIPAA, with respect to their PHI, include the right to access, amend, and account for disclosures. Doctors, hospitals, and all other health providers are required in the statute to adhere to the regulation outlined in HIPAA with respect to keeping the privacy and security of PHI belonging to patients.
Benefits of EDI 834 Process
- Streamlines and automates communication: The EDI 834 process reduces the chance of errors and accelerates data transfer. For instance, instead of manual data entry, the standardized EDI 834 file format enables smooth transmission of enrollment and maintenance information. Ultimately, it minimizes the potential for mistakes caused by human error.
- Data Security: The 834 transaction processing enhances data accuracy, due to the standardization of the EDI 834 file format following strict ANSI X12 EDI guidelines. This standardization ensures consistent and precise data exchange between parties, eliminating the need for manual data entry. As a result, it reduces the risk of inaccuracies.
- Minimizes administrative expenses: The process’s automated nature frees up time and resources. As a result, it reduces overhead costs, lowers labor expenses, and increases efficiency.
Challenges with EDI 834 Processing
Outsourcing the EDI solutions to the top EDI solution providers would help in eliminating the 834 challenges as below:
- Good understanding of the 834 format, as well as the technical capabilities to implement it properly
- Continuous human intervention sometimes leads to errors.
- The information contained within the format can differ from carrier to carrier even after a standardized format and the same health insurance plan. This can lead to difficulties in transferring data between carriers and can increase the risk of errors.
- -Many companies have experienced black box in 834 experiences. Therefore, it makes it difficult to enable custom enrollment policies and rules in the software.
- -Tedious and complicated monthly file processing in bulk, especially during the open enrollment period.
- -The process requires specialized software and hardware, as well as trained personnel to implement it.
Moreover, Implementing EDI can be a substantial investment for insurance sponsors and payers, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- -There is a waste of time in eliminating the invalid or corrupt formatted files.
- -Files such as transaction type and member record, that are logically out of order lead to inaccuracies in membership records.
- -The software logic determines the delta transactions when an entire 834 EDI membership snapshot files are shared for processing
- -The sensitive nature of healthcare data requires its security & protection.
X12 EDI 834 Mapping & Translation
Modern EDI providers, like A3Logics, offer end-to-end EDI solutions consisting of EDI mapping and translations, secure methods of file transmission with partners, and backend integration to simplify the transformation flows.
Other Healthcare Transactions
- EDI 837: Healthcare Claim Transaction
- EDI 835: EDI Healthcare Claim Payment
- EDI 820: EDI Payroll Deducted / Group Premium Payment for Insurance Products
- EDI 270: Healthcare Eligibility/Benefits enquiry
- EDI 271: Health Care Eligibility/Benefit Response
- EDI 276: Health Care Claim Status Request
- EDI 277: Health Care Claim Status Response
- EDI 278: Health Care Service Review Information
- EDI 997: Functional Acknowledgement Transaction Set
Ensure Accurate Enrollment by Joining our Leaders in EDI 834 Solutions
Conclusion
834 file contains information about the payer, sponsor, and the member involved in offering a benefits product. Insurance agencies, government agencies, unions, and employers use this transaction set to enroll their staff members in employee benefits administration solutions. The Healthcare Industry uses this standard most widely. Additionally, it follows the specific HIPAA 5010 standards for electronic data exchange.
834 EDI is also the core of the enrollment and maintenance transaction between insurers and federal and state exchanges. To change or replace the 834 formats, Congress has to introduce a new standard. As government agencies have many regulations requiring re-configuring all state and federal exchanges, we expect 834 to stay for a very long time.