Artificial Intelligence has pervasively transformed medical diagnosis and created unparalleled avenues to optimize patient care efficiency. AI applications have transformed the medical diagnostic process by utilizing intricate algorithms with machine learning in healthcare methods to identify medical conditions more rapidly and accurately than previously explored. The utilization of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis has grown in popularity in response to the problems it has been trying to solve for many years in healthcare systems. According to a study by Icenur, AI-driven innovations will generate $150 billion in annual savings for the United States healthcare economy by 2026.
AI in an industry’s patient care machinery is worth $489 billion today, and this level of value reveals how effective the system-generated savings are. Another major benefit of using artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis is the system’s ability to analyze vast amounts of patient data in record time and with high accuracy. For instance, AI-driven imaging solutions can quickly identify abnormalities in medical scans, developing them quicker, thereby enabling healthcare workers to begin treatment much sooner.
Furthermore, the system can evaluate patterns and commonalities among patient records, allowing for individualized treatment plans. Furthermore, AI has been instrumental in identifying diseases at a much earlier stage, which would ideally result in implementing successful prevention strategies. In some cases, software development outsourcing services have exceeded human clinicians’ knowledge in certain activities, reducing the onset of common diseases such as cancer or the cardiovascular system by analyzing radiology, pathology, and other health records. With healthcare increasingly in demand and resources constrained, incorporating artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis appears poised to create better patient care outcomes.
Transform Your Healthcare Software Vision into Reality – Book A 30 Minutes Free Consultation!
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis
Artificial Intelligence has the potential to change the face of medical diagnosis. AI, with the use of advanced scientific algorithms and machine learning, may help to increase diagnostic effectiveness, support workflow, and improve patient outcomes. In recent years, there have been substantial improvements in AI technology that have enabled its extensive application in medicine. AI techniques may analyze medical photographs as well as interpret fundamental clinical data and, vice versa, have a broad application in verifying the accuracy of diagnostics. Given these current capabilities and persistent constraints in healthcare delivery, we expect AI to offer promise in altering traditional diagnostic practices in the foreseeable future.
AI’s ability to digest immense volumes of medical data with astounding speed and precision is a primary propeller of its effectiveness in medicinal diagnosis. By scrutinizing affected person records, visualization reports, and hereditary facts, Artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis can notice subtle patterns and connections that would possibly slip past human observation. This potential not only accelerates the diagnostic technique but also increases diagnostic accuracy, resulting in more timely and powerful interventions. Moreover, AI-enabled diagnostic tools have exhibited outstanding overall performance in identifying diseases at early levels, when remedy outcomes are most auspicious.
As healthcare systems worldwide struggle under mounting pressure, AI presents an innovative way to boost diagnostic abilities and better utilize limited resources. When partnering with providers, AI can both analyze anomalies and recognize patterns to aid in diagnosis, assisting some cases more quickly while freeing up time to tackle complex issues requiring human intuition. By enhancing professionals instead of replacing them, technology expands ability to gainfully reshape workflows, minimize mistakes, and fundamentally strengthen the care experience for all.
What is The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis?
Artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis is acquainting creative techniques with better pinpoint ailments and make therapy available to additional people. Advanced algorithms and machine learning unleash AI’s potential to reshape conventional diagnostic methods and augment what medical professionals can provide through their care. Some exams involve only brief glimpses, yet AI digs deeper, aware of obscure hints and subtle signs. Where humans consider solitary clues, AI joins varied clues across specialties into a nuanced perspective. Together, man and machine will solve more medical mysteries and help more patients.
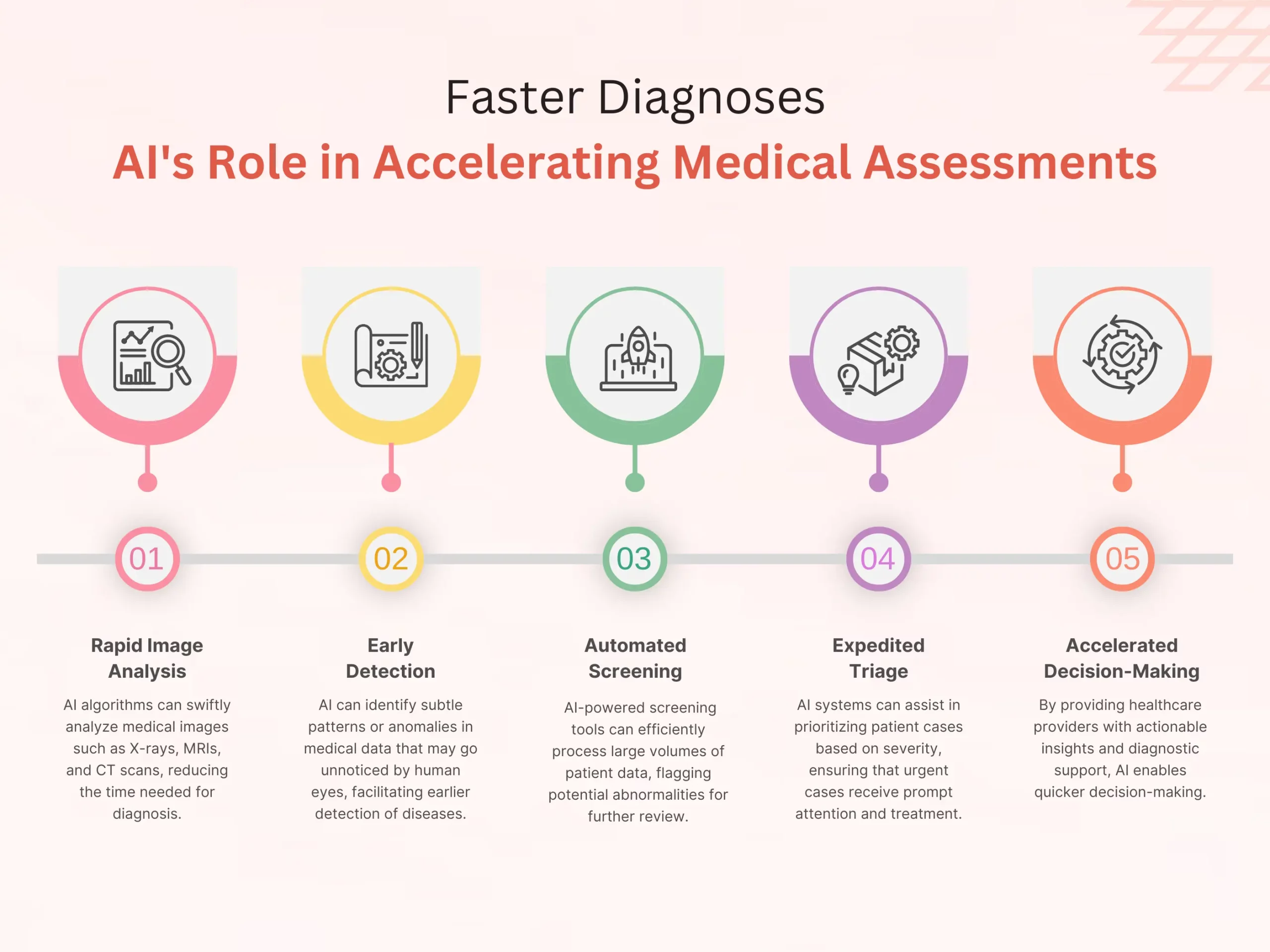
1. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
Firstly, AI algorithms are capable of analyzing all types of medical data, such as imaging studies, patient records, and genetic information, at incomparable speed and precision. AI algorithms reliably detect subtle patterns and anomalies that human senses would miss, leading to more accurate diagnoses.
2. Early Disease Detection
Secondly, AI-driven diagnostic tools excel at detecting diseases at the earliest stages of their development when intervention is more effective. AI tools analyze patient data and know their risk factors, detecting abnormalities and predicting disease onset to prevent its progression or at least slow its development.
3. Personalized Treatment Plans
AI facilitates the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs. By analyzing patient data, Custom Software Development Services USA includes genetic profiles and treatment responses, AI systems can recommend optimal treatment strategies, leading to improved therapeutic outcomes and patient satisfaction.
4. Streamlined Workflows
AI technology smoothes out diagnostic workflows via automating dull errands and giving decision support to medical services experts. This lessens the weight on clinicians as well as speeds up the diagnostic cycle, prompting quicker completion times and improved patient throughput.
5. Improved Accessibility
AI-driven diagnostic devices can possibly further develop medical services accessibility, especially in underserved or far off regions. By utilizing telemedicine stages and portable applications, AI-empowered diagnostics can expand the scope of medical care services, empowering ideal diagnosis and therapy for people with restricted admittance to conventional medical care offices.
6. Continuous Learning and Improvement
AI systems can continuously learn and adjust in view of criticism and new information. This empowers AI calculations to advance, working on diagnostic precision and adequacy through iterative learning processes.
7. Integration with Clinical Decision Support Systems
Custom software development services can upgrade their diagnostic capabilities via consistently coordinating AI technology with existing clinical decision support systems. By giving ongoing bits of knowledge and proposals, AI-driven decision support instruments engage clinicians to settle on more educated diagnostic and treatment choices.
The job of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis is complex, enveloping upgraded diagnostic precision, early sickness location, customized therapy arranging, streamlined workflows, improved accessibility, continuous learning, and integration with clinical decision support systems. Finally, by utilizing the capabilities of AI, medical care suppliers can work on quiet results, advance asset usage, and at last change the conveyance of medical care services.
The Evolution of AI in Healthcare
The evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare represents a groundbreaking excursion from hypothetical ideas to down to earth applications, reshaping the scene of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis, treatment, and patient consideration. At first, the essential focal point of generative AI in healthcare was innovative work, with early analyses tracing all the way back to the
Benefits of Using GenAI in Healthcare
Generative AI (GenAI) presents a large number of advantages in changing healthcare services, offering extraordinary solutions that upgrade diagnostics, therapy procedures, patient consideration, and general functional proficiency.
1. Accuracy Diagnostics:
Generative AI in Healthcare altogether improves analytic exactness in healthcare imaging translation. Studies have demonstrated that artificial intelligence-based systems, utilizing generative models, further develop exactness rates by up to 30% in distinguishing irregularities in radiology filters, such as X-beams, X-rays, and CT examines. This accuracy supports early infection discovery, prompting convenient mediation and working on persistent results.
2. Sped-up Medication Disclosure:
The use of GenAI assists the medication disclosure and advancement process. By utilizing AI and generative models, analysts can foresee compound connections, mimic medication reactions, and recognize potential medication competitors all the more quickly.
This approach lessens drug disclosure timetables by 30-half and brings improvement costs down to 60%, altogether affecting the accessibility of new treatments.
3. Customized Treatment Methodologies:
GenAI works with the production of customized therapy plans by examining different patient data collections, including hereditary data, healthcare history, and treatment reactions. The combination of these bits of knowledge empowers artificial intelligence models to produce custom-fitted treatment choices. Reception of artificial intelligence-driven customized treatment plans has shown a 25% decrease in unfavorable impacts and a 20% improvement in treatment results.
4. Upgraded Patient Care:
Artificial intelligence-driven tools, for example, chatbots and remote helpers controlled by Generative AI, improve patient consideration by offering ceaseless help, noting inquiries, and offering healthcare direction.
More than 70% of healthcare services suppliers coordinate artificial intelligence-fueled devices to smooth out persistent communications, lessen managerial weights, and guarantee convenient help, further developing Generative AI in Healthcare services.
5. Telemedicine advancements:
Telemedicine, reinforced by GenAI, has seen critical advancements. Far-off quiet checking and artificial intelligence-empowered diagnostics work with healthcare services deliverance past conventional healthcare care settings.
This approach empowers more productive distribution of assets, stretches out healthcare benefits to far-off regions, and further develops admittance to healthcare care, particularly in underserved networks.
6. Factual Insights:
- The worldwide artificial intelligence in the Healthcare market is projected to outperform $67.4 billion by 2027, exhibiting the fast reception and development of artificial intelligence-driven advances in the healthcare area.
- Artificial intelligence-controlled devices are assessed to lessen healthcare care costs by up to half while working on quiet results, as detailed by a few analyses.
Future Possibilities:
Generative AI technology keeps on developing, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence algorithms and the accessibility of huge healthcare datasets. A joint effort between artificial intelligence consultants, healthcare services experts, and administrative bodies is vital for enhancing artificial intelligence’s true capacity while guaranteeing moral practices, patient protection, and administrative consistency.
GenAI’s direction in healthcare care is ready to reclassify healthcare practices, fuel development, and further develop healthcare services deliverance on a worldwide scale. As artificial intelligence innovations keep on propelling, their effect on healthcare services vows to reform patient consideration, improve asset use, and at last upgrade health results for populaces around the world.
Use Cases of GenAI in Healthcare
Generative AI opens up the chance for a lot of new use cases for different organizations to robotize, increase, and improve manual cycles and subsequently assist with further developing client experience and representative efficiency. A few organizations are likewise creating healthcare services and healthcare space explicit models, for example, Drug PaLM from Google, BioGPT, healthcareBERT, and GatorTron from the College of Florida and Nvidia. These models are prepared in the Healthcare services space to give exact responses to the inquiries.
Healthcare services, Pharma, and healthcare devices organizations are assessing the innovation and investigating business use cases to apply this innovation as there is an enormous potential for Generative AI to assist with working on quiet consideration and experience, healthcare independent direction, diminish healthcare services proficiency responsibility, accelerate healthcare exploration and improve functional effectiveness.
Medical Note-Taking
Generative AI can smooth out and robotize the healthcare note-taking cycle by catching the vital realities from patient discussions and summing them up as doctors’ notes in Electronic Health Records.
It can likewise be utilized to sum up and make healthcare notes, for example, visit synopses, release notes, radiology reports, or pathology reports. The machine learning solutions can likewise improve complex healthcare language into rundowns and interpret them into any language so patients can see without any problem.
Clinical Decision Support
Generative AI can help specialists and healthcare experts make exact and informed analyses and propose therapy choices by breaking down data from a patient’s healthcare records, lab results, past therapies, and healthcare imaging, like X-rays and X-beams. It can likewise help in quiet schooling by addressing questions connected with sickness and therapy.
Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring
ChatGPT-based remote helpers can assist patients with booking solutions, getting treatment, and dealing with their health data. It can likewise be utilized to screen patients from a distance by examining data from wearables, sensors, and other checking devices, giving continuous experiences into a patient’s health status to healthcare services suppliers.
Medical Data and Education
Patients can speak with ChatGPT utilizing regular language and pose inquiries connected with drugs, including dose, incidental effects, and communications. ChatGPT can likewise furnish understudies and healthcare services experts with moment admittance to the most recent exploration, rules, and practices, accordingly supporting their continuous learning and advancement.
Drug Discovery and Development
The utilization of GenAI can speed up the medication revelation and advancement process. Via looking through the healthcare and logical writing on sites, like PubMed or healthcaretrials.gov, potential medication up-and-comers can be distinguished and tried for adequacy utilizing programmatic experiences (in silico) before continuing to Generative AI preliminaries on creatures and people.
GenAI can plan healthcare preliminaries and creator convention archives. It can likewise make healthcare review reports by producing synopses of healthcare preliminaries, including the review plan, patient attributes, adequacy and health results, and measurable analysis. This can altogether lessen the time and exertion expected to physically aggregate this data.
Healthcare device submission
GenAI can be utilized to consequently make vital Premarket Endorsement (PMA) applications or Premarket Notice 510(k) documentation for FDA Accommodation. It can likewise be possibly utilized for making naming documentation.
By examining data from healthcare devices, for example, imaging hardware or ventilators, GenAI algorithms can predict when upkeep is fundamental. This can assist healthcare care suppliers with enacting their production network processes before proactively keeping up with their gear and lessen the gamble of hardware disappointment.
Synthetic Medical Data
GenAI can assist with creating manufactured patient-level healthcare data that is sensible to prepare Top AI models without the gamble of uncovering private data about genuine patients.
. Nonetheless, critical headways in processing power, information availability, and algorithmic complexity have pushed AI from the domain of scholastic examination to certifiable clinical settings.
In the beginning phases of AI reception in healthcare, its application was restricted by mechanical constraints and distrust from the medical local area. Notwithstanding, as registering capabilities improved and proof of AI’s potential advantages amassed, healthcare stakeholders started to perceive its worth in tending to handle difficulties like diagnostic accuracy, treatment optimization, and healthcare accessibility.
Throughout the long term, AI in healthcare has seen a quick evolution, set apart by outstanding achievements and leap forwards. From IBM’s Watson diagnosing uncommon illnesses to Google’s DeepMind foreseeing patient disintegration, AI advances have exhibited surprising capabilities in different domains of healthcare. Moreover, the integration of AI with other arising advances, like large information, genomics, and wearable gadgets, is opening new avenues in healthcare development. By utilizing enormous volumes of healthcare information and progressing investigation, the healthcare learning management system can create significant experiences, work with accurate medication draws near, and empower proactive healthcare mediations.
AI is ready to extend its effect on healthcare, driving improvements in quiet results, functional productivity, and healthcare conveyance as it keeps on advancing. However, difficulties like information security, administrative consistency, and moral contemplations remain significant contemplations in the continuous evolution of AI in healthcare.
Transform Your Business Custom Healthcare Solutions. Request a Free Consultation Today!
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis for Patient Care
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has arisen as a transformative force in medical diagnosis, offering a large number of advantages that upgrade patient consideration and revolutionize healthcare conveyance. By utilizing progressed calculations and AI methods, AI systems are enlarging the diagnostic capabilities of healthcare experts, prompting improved results, expanded effectiveness, and enhanced patient encounters.
1. Enhanced Diagnostic Accuracy
Right off the bat, AI-driven diagnostic instruments succeed at breaking down huge measures of medical information with unmatched speed and accuracy. By identifying unobtrusive examples and peculiarities that might evade human insight, AI calculations altogether upgrade diagnostic accuracy, decreasing the probability of misdiagnosis and guaranteeing suitable treatment plans.
2. Early Disease Detection
Also, AI-empowered diagnostic systems have exhibited amazing execution in identifying diseases at their earliest stages, when mediation is best. By breaking down quiet information and recognizing risk factors, AI calculations can distinguish irregularities and anticipate disease beginning, empowering ideal mediations to forestall or moderate disease movement.
3. Personalized Treatment Plans
AI works with the development of personalized treatment plans tailored to individual patient necessities. By examining patient information, including hereditary profiles, medical history, and treatment reactions, AI calculations can suggest ideal treatment procedures that augment helpful results while limiting unfriendly impacts by dissecting patient information, prompting improved patient results and fulfillment for custom software development companies in USA.
4. Streamlined Workflows
AI technology smoothes out diagnostic workflows via automating tedious undertakings and giving decision support to healthcare experts. This decreases the weight on clinicians as well as speeds up the diagnostic interaction, prompting quicker times required to circle back and improved patient throughput.
5. Improved Resource Allocation
AI-driven diagnostic apparatuses streamline resource allocation by focusing on cases in light of seriousness and direness. By triaging patients and designating resources all the more proficiently, AI assists healthcare suppliers with conveying convenient consideration to the people who need it most, consequently working on persistent results and upgrading healthcare conveyance.
6. Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine
AI-controlled diagnostic systems empower remote monitoring and telemedicine, permitting healthcare suppliers to screen patients’ wellbeing status remotely and intercede quickly when vital. This upgrades accessibility to healthcare services, especially for people in remote or underserved regions, and decreases the requirement for in-person visits, working on quiet accommodation and fulfillment.
7. Continuous Learning and Improvement
AI systems can continuously learn and adjust in light of criticism and new information. Finally, This empowers AI calculations to advance, working on diagnostic accuracy and viability through iterative learning processes, at last prompting better understanding of the results.
Real-world Applications of AI in Enhancing Patient Care Efficiency
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has progressed from a hypothetical idea to a useful reality in healthcare, with genuine applications that are revolutionizing patient consideration conveyance. By saddling the force of cutting edge calculations and AI methods, AI is driving efficiencies across different parts of healthcare conveyance, prompting improved patient results and enhanced healthcare encounters.
1. Medical Imaging Analysis
Right off the bat, AI-fueled calculations are changing the field of medical imaging analysis, empowering more precise and productive translation of diagnostic pictures like X-beams, X-rays, and CT filters. AI systems can identify unpretentious anomalies, help radiologists in focusing on cases, and decrease the time expected for diagnosis, at last further developing patient consideration effectiveness.
2. Clinical Decision Support Systems
Furthermore, Artificial intelligence diagnosis medical decision support systems furnish healthcare suppliers with continuous bits of knowledge and suggestions in view of patient information, medical writing, and best practices. These systems assist clinicians with settling on more educated diagnostic and treatment choices, prompting better patient results and decreased changeability in care conveyance.
3. Predictive Analytics for Disease Management
AI calculations examine huge datasets of patient data to recognize examples and patterns related with disease beginning, movement, and treatment reaction. By anticipating future wellbeing results and distinguishing people at high gamble of fostering certain circumstances, AI works with proactive mediations, preventive consideration techniques, and personalized treatment plans, along these lines further developing patient consideration productivity and results.
4. Remote Patient Monitoring
AI-empowered remote patient monitoring advances permit healthcare suppliers to follow patients’ wellbeing status and important bodily functions beyond customary healthcare settings. By remotely monitoring patients with ongoing circumstances or recuperating from a medical procedure, artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis identifies early admonition indications of weakening, forestalls superfluous clinic readmissions, and advances patient self-management, prompting improved care proficiency and decreased healthcare costs.
5. Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Clinical Documentation
AI-controlled NLP innovations automate the clinical documentation process by changing over communicated in or composed language into organized information. By removing pertinent data from medical notes, reports, and records, AI smoothes out authoritative workflows, diminishes documentation mistakes, and opens up clinic contract management software time for direct patient consideration, in this way improving consideration proficiency.
6. Personalized Medicine and Treatment Optimization
AI examines individual patient qualities, including hereditary profiles, medical history, and way of life factors, to tailor treatment plans and mediations to every patient’s one of a kind requirements. By advancing treatment regimens and drug doses in light of patient-explicit variables, AI further develops treatment viability, limits unfriendly impacts, and improves patient fulfillment and adherence.
7. Healthcare Resource Allocation and Optimization
AI-driven predictive analytics models break down healthcare use information, patient stream examples, and resource availability. By anticipating patient interest, recognizing bottlenecks, and upgrading resource usage, AI helps healthcare software development services work on functional effectiveness, lessen wait times, and improve patient admittance to mind.
This present reality uses of AI in healthcare are different and effective, spreading over medical imaging analysis, clinical decision support, predictive analytics, remote patient monitoring, documentation automation, personalized medicine, and healthcare resource optimization. Finally, by utilizing AI advances, healthcare suppliers can smooth out workflows, work on diagnostic accuracy, improve treatment results, and eventually convey more productive and patient-focused care.
Challenges of Integrating Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis
While Artificial Intelligence (AI) holds massive commitment for changing Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis and improving patient care, its integration into clinical practice presents a few cons of AI in healthcare that should be tended to. From data privacy worries to regulatory obstacles, healthcare associations face different hindrances to bridling the maximum capacity of AI in diagnostic settings.
1. Data Quality and Accessibility
Right off the bat, One of the essential challenges in integrating artificial intelligence into medical diagnosis is the quality and accessibility of healthcare data. AI calculations require huge volumes of great data for training and approval, yet healthcare data frequently experiences inconsistencies, errors, and interoperability issues. Guaranteeing the availability of spotless, normalized data is fundamental for the fruitful execution of AI-driven diagnostic arrangements.
2. Data Privacy and Security
Besides, Healthcare data are profoundly delicate and dependent upon severe privacy guidelines, for example, the Health care coverage Transportability and Responsibility Act (HIPAA) in the US. Safeguarding patient privacy and guaranteeing data security are central worries while integrating AI into medical diagnosis. Healthcare associations should execute strong data encryption, access controls, and privacy strategies to shield patient data against unapproved access and breaks.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Certification
AI-driven medical gadgets and diagnostic calculations are dependent upon regulatory oversight by government organizations like the Food and Medication Organization (FDA) in the US. Obtaining regulatory endorsement for AI-based diagnostic arrangements can be a complex and tedious interaction, requiring broad clinical approval studies and adherence to rigid quality confirmation principles. Exploring the regulatory scene represents a critical test for healthcare learning management systems looking to send AI in clinical practice.
4. Interpretable and Explainable
AI calculations frequently work as “secret elements,” pursuing it trying to decipher their choices and figure out the basic thinking behind diagnostic suggestions. Guaranteeing AI-driven diagnostic results are interpretable and explainable. This is significant for gaining the trust of healthcare suppliers and patients. Creating straightforward and interpretable AI models that give understanding into their decision-production process is fundamental for encouraging acknowledgment and reception in clinical settings.
5. Bias and Fairness
AI calculations may unintentionally sustain biases present in the data utilized for training, prompting variations in diagnostic accuracy and treatment suggestions across various patient populaces. Tending to algorithmic bias and guaranteeing fairness in AI-driven diagnostic systems is fundamental for advancing evenhanded healthcare results. Healthcare associations should execute measures to identify and moderate bias in AI calculations, like assorted training data portrayal and algorithmic fairness appraisals.
6. Integration with Existing Workflows
Adding AI to clinical workflows has strategic challenges. These incorporate similarity with electronic health record (EHR) systems, interoperability with other healthcare IT, and integration with suppliers’ existing practices. Consistent integration of AI-driven diagnostic devices into clinical workflows is fundamental for limiting interruption and amplifying the productivity gains related with AI reception.
Adding AI to medical diagnosis is promising. It can work on patient care. Notwithstanding, healthcare associations should address challenges. They are connected with data quality, privacy, rules, interpretability, bias, and work process. In conclusion, To defeat these challenges, healthcare suppliers, technology designers, policymakers, and controllers should cooperate. They should guarantee that AI-driven diagnostic arrangements are sent dependably and actually in clinical practice.
Unlock Your Business Potential with Custom Software Solutions. Contact us Today!
Ethical Considerations and Patient Privacy in Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis
Artificial intelligence (AI) has arisen as a promising device in medical diagnosis, offering the potential to reform healthcare by upgrading exactness, productivity, and openness. AI algorithms, especially machine learning in healthcare models, have exhibited astounding capacities in deciphering medical pictures, breaking down patient data, and recognizing designs that could escape human discernment. Yet, AI in healthcare raises huge ethical issues. These are about patient security and data protection. The healthcare business depends more on AI for diagnosis and treatment. Tending to these ethical concerns is essential. This is expected to guarantee patient trust, confidentiality, and autonomy.
1. Patient Confidentiality
AI frameworks, first and foremost, frequently need heaps of patient data. This data incorporates medical records, imaging filters, and hereditary data. They use it to train and get to the next level. Be that as it may, maintaining patient confidentiality is fundamental to maintaining trust between healthcare suppliers and patients. Ethical AI rehearses should put data anonymization, encryption, and secure stockpiling first. This means safeguarding touchy data from unapproved access or abuse.
2. Informed Consent
Besides, Patients reserve the option to understand the utilization of their data in AI-driven medical diagnosis and therapy. Informed consent instruments ought to be carried out to guarantee that patients are completely mindful of the dangers, advantages, and potential ramifications of AI advancements for their healthcare. This incorporates transparency with respect to data-sharing practices, algorithmic biases, and the chance of mistakes or misdiagnoses.
3. Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
AI algorithms can acquire biases in the training data. This prompts differences in diagnosis and treatment across segment gatherings. Tending to algorithmic bias requires cautious thought of data portrayal, variety, and fairness measurements during calculation development. Ethical AI structures ought to battle bias. They ought to advance fair healthcare for all patients. This incorporates patients of any race, nationality, orientation, or pay.
4. Data Security and Governance
The expansion of AI in healthcare requires vigorous data security measures to forestall breaks, unapproved access, and cyberattacks. Healthcare associations should set clear governance structures. They should likewise set consistency systems. These designs and systems guarantee adherence to data protection rules. The standards incorporate the Health care coverage Versatility and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the US. Moreover, organizations between healthcare suppliers and hire software developers ought to focus on ethical data-sharing practices and lay out conventions for data access, utilization, and maintenance.
5. Accountability and Transparency
Being clear about, as far as possible, and dangers of AI in medical diagnosis is critical. It assembles trust among patients, specialists, and controllers. Healthcare software development services ought to execute instruments for observing and reviewing AI frameworks, including following execution measurements, recording dynamic cycles, and giving clarifications to algorithmic results. Likewise, setting up accountability structures can assist with decreasing risk concerns. They guarantee accountability for mistakes or terrible results from AI healthcare.
6. Patient Empowerment and Autonomy
While AI advancements hold the commitment of working on symptomatic exactness and clinical direction, they ought to expand instead of supplant the job of healthcare experts. Patients ought to control their healthcare choices. They ought to approach clear clarifications and choices when AI gives proposals. Furnishing patients with data and including them in the dynamic cycle can further develop trust, fulfillment, and adherence to treatment plans.
7. Ethical Guidelines and Regulatory Oversight
Creating and complying with ethical guidelines and regulatory structures is fundamental for directing the capable arrangement of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis. Policymakers, healthcare experts, AI developers, and ethicists should cooperate. They are expected to set clear standards for data protection, informed consent, fair algorithms, and accountability in AI healthcare. To address the extraordinary difficulties of AI, regulatory organizations ought to adjust existing regulations. They need to maintain patient freedoms and morals in the quick changing landscape of healthcare development.
While artificial intelligence holds immense potential to transform medical diagnosis and work on patient results, ethical contemplations should support its mix into healthcare frameworks. In conclusion, It is critical to Focus on patient protection. So are informed consent, fairness, transparency, accountability, and regulatory consistency. This center is fundamental to assemble trust, cut chances, and get every one of the advantages of utilizing AI to further develop healthcare.
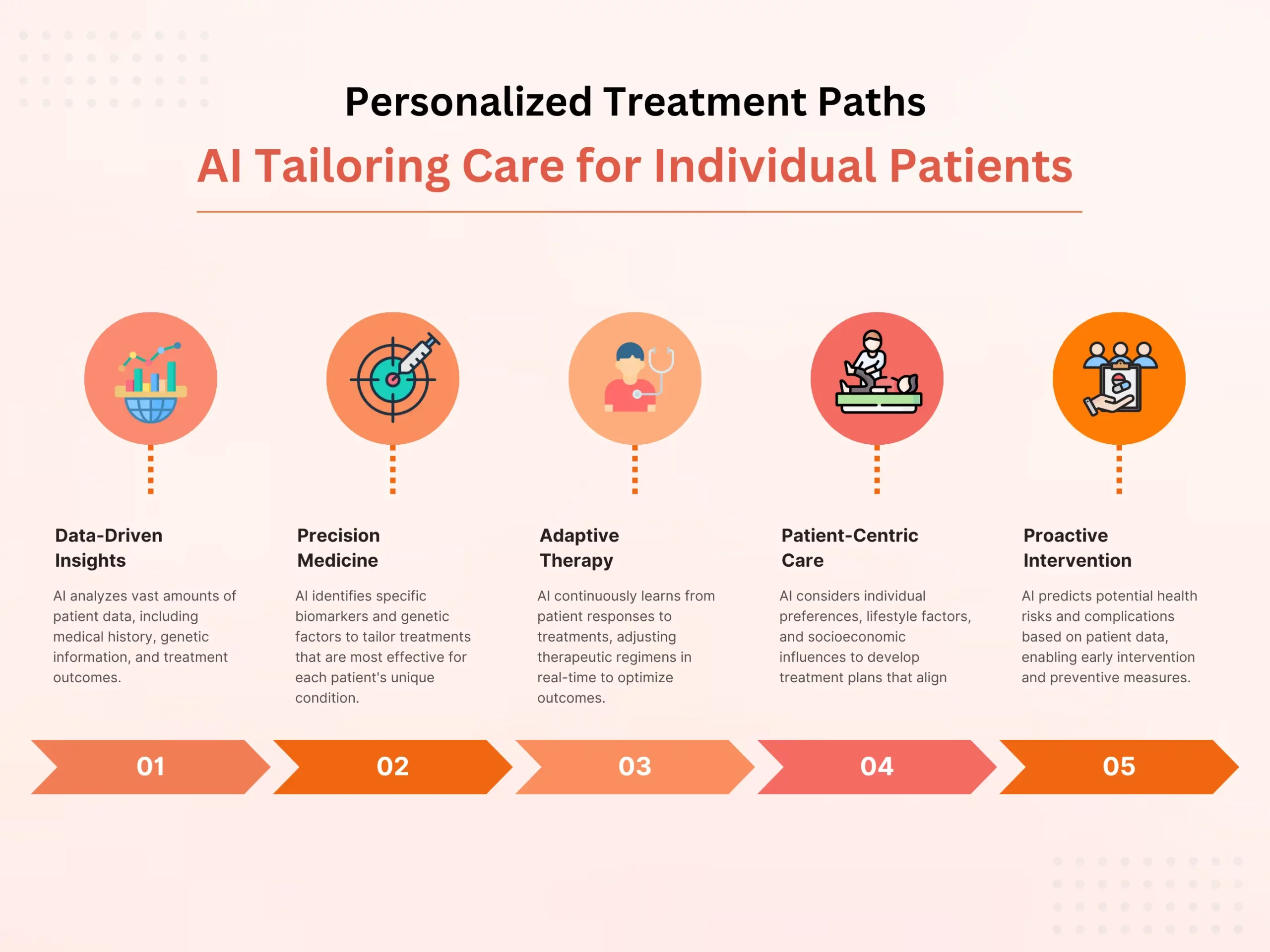
Strategies for Healthcare Providers to Adopt AI to Improve Patient Care
As the healthcare scene advances, healthcare providers are progressively going to artificial intelligence (AI) to upgrade patient consideration, smooth out clinical work processes, and further develop results. AI advances offer inventive solutions for diagnosing infections, customizing treatment designs, and enhancing healthcare conveyance. Be that as it may, fruitful integration of AI into healthcare rehearses requires cautious preparation, key execution, and collaboration among partners. In this unique circumstance, healthcare providers can utilize numerous procedures. These will allow them to utilize AI well while tackling issues and amplifying patient consideration benefits.
1. Investment in AI Infrastructure
First and foremost, Healthcare providers need to put resources into strong AI infrastructure, including equipment, software, and data stockpiling abilities, to support the execution and sending of AI advances. This might include overhauling IT systems. It might include getting AI instruments and stages. It might likewise include making associations with tech sellers or examination establishments. These organizations are to get to state of the art AI solutions.
2. Data Collection and Integration
Also, AI calculations depend on top notch, different datasets for training and approval. Healthcare providers ought to zero in on data collection. They ought to utilize electronic health records (EHRs), clinical imaging documents, and wearable gadgets. They ought to utilize these instruments to accumulate full persistent data. Coordinating unique data sources and normalizing data designs are fundamental stages to guarantee data interoperability and openness for artificial intelligence in software development.
3. Collaboration with AI Experts
Healthcare providers can profit from teaming up with AI experts, including data researchers, machine learning specialists, and domain-explicit analysts, to foster tweaked AI solutions tailored to their clinical requirements. Interdisciplinary groups can utilize ability from healthcare and tech. They use it to configure, test, and send AI calculations well. They do this while tending to domain-explicit difficulties and cutoff points.
4. Clinical Decision Support Systems
AI-controlled clinical decision support systems (CDSS) can help healthcare providers. They do this by giving ongoing bits of knowledge, forecasts, and proof based proposals at the mark of care. CDSS can assist with diagnosing illnesses. It can foresee treatment results and distinguish personalized intercessions. It utilizes patient-explicit data and clinical rules.
5. Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
AI innovations can ease telemedicine and remote monitoring drives by empowering virtual interviews, remote patient monitoring, and prescient investigation for early mediation. custom software development outsourcing services can use AI-fueled chatbots, menial helpers, and remote monitoring gadgets to convey personalized care, screen patient advancement, and enhance asset designation in remote or underserved regions.
6. Continuous Learning and Improvement
AI calculations need continuous learning and refinement. They should adjust to changing clinical situations, patient gatherings, and healthcare rehearsals. Healthcare providers ought to lay out instruments for gathering criticism, assessing calculation execution, and further developing AI models in view of genuine data and clinical bits of knowledge. This iterative methodology guarantees that AI in clinical conclusion stays precise. It is likewise dependable and state-of-the-art. This is key in unique healthcare.
7. Ethical and Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare providers should stick to ethical standards and regulatory necessities while adopting AI innovations to guarantee patient protection, data security, and algorithmic fairness. Setting clear principles for data administration, informed assent, calculation straightforwardness, and responsibility is vital. It diminishes dangers and constructs trust among patients, healthcare laborers, and controllers.
8. Education and Training
Training healthcare experts on generative AI in healthcare essentials, including data education, algorithmic understanding, and ethical contemplations, is critical for fruitful AI reception. Healthcare providers ought to put resources into education. This implies projects, studios, and confirmation courses. They are to enable clinicians, nurture, and unified healthcare experts. These projects will give them the information and abilities expected to utilize AI well in their training.
Adopting AI for better quiet consideration requires an essential methodology. Ultimately, by embracing AI capably and proactively tending to difficulties, healthcare providers can utilize AI’s maximum capacity. They can utilize it to propel the conveyance of superior grade, personalized healthcare.
Future Prospects: The Potential Impact of AI on Patient Care Efficiency
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) can possibly change the efficiency of patient consideration in healthcare settings. AI-driven advances offer new opportunities to streamline clinical work processes. They likewise further develop analysis precision, customize treatments, and improve healthcare conveyance. Healthcare providers can utilize machine learning, normal language handling, and predictive analytics. This can smooth out processes, cut regulatory weights, and assign resources better. In this specific circumstance, investigating the possibilities of AI in tolerant consideration efficiency is fundamental for grasping the valuable open doors, and cons of AI in healthcare, and the ramifications of coordinating AI into healthcare systems.
1. Automation of Routine Tasks
Right off the bat, AI calculations can automate routine managerial tasks. These incorporate arrangement planning, clinical record, and charging coding. This opens up healthcare experts’ opportunity to zero in on quiet consideration. Automation decreases manual mistakes. It additionally makes work processes more productive. It allows staff to invest more energy with patients. This prompts more joyful patients and better resource use.
2. Predictive Analytics for Early Intervention
Furthermore, AI can dissect a great deal of patient data. This data incorporates clinical records, tests, and wearable gadget measurements. It tracks down examples and patterns that show infection movement or disintegration. By utilizing predictive models, hospital risk management software can mediate proactively, carry out preventive measures, and advance treatment intends to alleviate risks and work on quiet results.
3. Personalized Treatment Recommendations
AI calculations can break down tolerant explicit data. This data incorporates hereditary profiles, clinical narratives, and treatment reactions. The calculations use it to make personalized treatment recommendations. The recommendations are tailored to individual requirements and inclinations. Personalized medication allows providers to convey designated interventions. It assists them with enhancing medicine regimens and lessen aftereffects. This prompts improved results and patient fulfillment.
4. Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
AI-fueled CDSS can help healthcare experts in clinical decision-production by giving proof based recommendations, rules, and alarms at the place of care. CDSS joins patient data with clinical information bases, clinical rules, and best practices. It supports analysis, treatment arranging, and illness management. This upgrades clinical exactness, efficiency, and adherence to conventions.
5. Telehealth and Remote Monitoring
AI advancements make telehealth and remote monitoring conceivable. They empower virtual consultations, remote patient monitoring, and telemedicine. Telehealth stages use AI calculations. They can emergency patients, do remote diagnostics, and give ongoing input to healthcare providers. They further develop care access, cut wait times, and lift patient accommodation and fulfillment.
6. Operational Efficiency and Resource Allocation
AI utilizes predictive, demonstrating and streamlining calculations. They can break down how healthcare offices work, patient stream, and resource use. This can upgrade efficiency and resource allocation. AI conjectures patient interest. It improves staffing and resource use. This empowers healthcare providers to further develop administration, cut wait times, and set aside cash. They can do this while keeping care quality.
7. Continuous Learning and Improvement
AI calculations require continuous learning and variation to advance clinical settings, patient populaces, and healthcare rehearses. Custom software development services can use criticism circles, true data, and execution measurements to iteratively further develop AI models, refine calculations, and upgrade their predictive precision, clinical importance, and ease of use after some time.
8. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
AI innovations are turning out to be more coordinated into healthcare systems. We should resolve ethical and regulatory issues. This is to guarantee patient protection, data security, and clear calculations. Healthcare providers should keep ethical rules and rules. They should likewise involve best practices for data administration, informed consent, and fair calculations. This is to diminish risks and assemble trust among patients, clinicians, and controllers.
AI could enormously affect patient consideration efficiency. Ultimately, by utilizing AI capably and handling difficulties, healthcare providers can open its maximum capacity. It can further develop patient consideration efficiency and healthcare results.
Ready to Build? Let’s Create Your Healthcare Software Solution Today!
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of AI for Improved Patient Care Efficiency
Harnessing the force of artificial intelligence (AI) presents a huge chance to reform patient care efficiency in healthcare settings. AI-driven tech can help healthcare providers. It allows them to upgrade clinical work processes, improve analysis, customize treatments, and smooth out activities. This all prompts better patient results and resource use.
The data shows the groundbreaking potential of artificial intelligence in medical diagnosis. For instance, the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) published a study. It found AI algorithms matched or even beat healthcare pros in diagnosing medical images. In addition, an Accenture report estimated that AI in healthcare software development could save the US healthcare economy $150 billion per year by 2026. This would come mainly from better efficiency and patient outcomes.
AI automates routine tasks, similar to arrangement planning and medical records. It diminishes authoritative weights and lets healthcare professionals center around direct patient care. Likewise, AI-controlled predictive analytics permit early intervention by finding designs that show how a sickness is deteriorating or advancing. This stops awful results and brings down the expenses of healthcare connected with hospital readmissions or crisis interventions.
AI calculations empower personalized medication. It tailors treatment to individual patient requirements. This advances treatment and lessens aftereffects. CDSSs give proof based recommendations at the mark of care. They improve precision and adherence to conventions.
Besides, telehealth stages fueled by AI empower remote consultations, diagnostics, and monitoring, further developing admittance to care and patient accommodation. Finally, AI-driven advancement calculations assist healthcare offices with anticipating patient interest, streamline resource allocation, and improve operational efficiency, at last upgrading administration conveyance and lessening costs.
Common Questions About Artificial Intelligence in Medical Diagnosis and Patient Care Efficiency(FAQs)
1. How does artificial intelligence improve medical diagnosis?
Artificial intelligence upgrades medical diagnosis by investigating huge datasets of patient data, including medical pictures, hereditary data, and clinical records. AI calculations can track down examples, oddities, and connections. These may not be clear to human clinicians. They lead to additional exact and ideal judgments. For instance, AI-controlled imaging systems can find issues in radiology examinations with high accuracy. This capacity takes into consideration early identification of sicknesses like malignant growth and lessens indicative blunders.
2. What are the benefits of using AI for patient care efficiency?
Using AI for patient care efficiency offers various benefits, including smoothed out work processes, improved indicative precision, personalized treatment designs, and enhanced resource allocation. AI-driven advances automate basic tasks. They are routine and regulatory. They let healthcare professionals center more around direct patient care. AI-fueled predictive analytics assist with early intervention. They do this by tracking down designs that show illness deteriorating. This reduces hospital readmissions and healthcare expenses.
3. How could healthcare providers at any point ensure the ethical utilization of AI in patient care?
Healthcare providers can ensure the ethical utilization of AI in patient care. They can do this by following standards like patient protection, data security, informed consent, and straightforward calculations. You should major areas of strength for execute administration strategies. They will ensure compliance with rules (e.g., HIPAA). You should likewise set clear rules for AI use and decision-production. These means are fundamental. Also, continuous monitoring, examining, and assessment of AI systems can assist with alleviating predispositions and ensure responsibility for custom software development companies in USA.
4. Could AI at any point replace human healthcare professionals in medical diagnosis and patient care?
Healthcare professionals can add to their abilities with AI. In any case, they shouldn’t replace human skill and judgment. AI calculations succeed at handling loads of data and tracking down designs. Yet, they miss the mark on human abilities of figuring out setting, compassion, and decisive reasoning. Healthcare providers assume a key part. They decipher AI-created experiences and use them in decision-production. They likewise give personalized care in light of patient requirements and inclinations.
5. What are the potential risks and challenges of AI in healthcare?
Potential risks and challenges related with AI in healthcare incorporate algorithmic predispositions, data security concerns, regulatory compliance issues, and the potential for overreliance on AI recommendations. Predispositions in calculations can prompt abberations in diagnosis and treatment results across various segment gatherings. Deficient data security might think twice about classification. Hospital management softwares should explore these challenges by carrying out ethical rules, powerful safety efforts, and continuous training and education for staff.