Table of Contents
EDI is a tool that’s useful even today for a business that aims to collaborate, optimize operations, and get ready to be competitive in today’s speed-of-light market. What does EDI stand for? EDI or Electronic Data Interchange is an important base technology for supply chain digital transformation and any business-to-business transformation. At the core, EDI offers a standardized platform for communication, thereby smoothing out relationships between trading partners. It helps to ensure that correct and proper information is made available to all participants in the supply chain.
Business partners can communicate structured documents and information by using EDI, a standardized electronic communication technology. Enabling the efficient, safe, and consistent computer-to-computer transmission of business documents is the goal of EDI. The global EDI software market is expected to grow from $1.98 billion in 2023 to $4.52 billion by 2030, at a compound annual growth rate of 12.5%. EDI makes automated data interchange between various computer systems possible and eliminates the need for conventional paper-based communication techniques.
This article examines the revolutionary potential of EDI integration methods for businesses, examining its advantages, practical applications, and essential elements. We’ll go over how it improves supply chain management and workflow efficiency, as well as how to integrate it practically and several approaches to common problems.

Understanding EDI
Businesses can exchange electronic documents and data in a common format by using the Electronic Data Interchange approach. This method differs greatly from conventional paper-based communication.
Using standardized standards, EDI integration facilitates the automatic exchange of business documents and data between companies. It expedites the transactions, cutting down on errors and manual labor while raising output levels all around. By making it easier for businesses to conduct business without the headache of manual data exchange and by enabling them to maintain appropriate relationships with trading partners, EDI technology has laid the groundwork for today’s business system. Even while EDI ERP integration isn’t enterprise resource planning (ERP), it is an ERP technique nonetheless.
The Five Essential Elements of EDI
By automating business procedures and optimizing data transfer, the EDI system can completely change your organization and make it easier to do business with you. But how precisely does EDI function? Excellent query. These are the five essential elements. When assessing your EDI alternatives, keep these things in mind.
1. Adaptable Interaction
Every possible trading partner will have an authorized EDI communication channel of their own. These techniques range from private value-added networks and secure file transfer protocols to AS2 EDI communication protocols. Ensure that your EDI solution is adaptable enough to fulfill all current and future communication needs.
2. Machine Translation
Without the need for manual intervention, your EDI solution should be able to validate and process received documents following industry standards. This includes the ability to issue Functional Acknowledgments (FAs) as digital receipts and to verify compliance.
3. Uncomplicated Data Administration
Consistent data interchange with trading partners necessitates constant monitoring and care. However, with the appropriate EDI solution, this management ought to be made easier and more efficient. For effective management, a dashboard that is easy to use and has built-in notifications is crucial. It makes it simple for you to keep an eye on your EDI transaction types and to swiftly detect and address any potential problems.
4. Smooth Incorporation
Your electronic data interchange software must be coupled with your transportation management system, warehouse management system, enterprise resource planning system, and any other pertinent software to guarantee smooth automation of your business activities. You may set up this integration with the assistance of a skilled and knowledgeable EDI partner, enabling automated workflows and doing away with human data entry.
5. Perfect Charting
Translating EDI transactions into forms that your back-office systems can easily understand is necessary to handle the continuous flow of EDI data. This mapping process is very important. When comparing EDI solutions and providers, it’s critical to check for mapping as a service, which is provided by many electronic data interchange companies.
The Function of EDI Integration
In today’s hectic business world, EDI-integrated business solutions help to increase competitiveness and operational efficiency. Smooth data flows throughout the supply chain can be facilitated via EDI integration methods, which link various corporate systems and trading partners. Businesses may use this connectivity to get precise information whenever they need it to stay ahead of the competition and make well-informed decisions.
With EDI integration methods, manual data entry is not necessary. This expedites the processing of transactions while lowering the possibility of human error. Important business papers like purchase orders, invoices, and shipment alerts can be exchanged more quickly and reliably. This is by enabling better communication between companies and their trading partners. As a result, companies can better manage their inventories, react to market demands more quickly, and—most importantly—raise consumer happiness.
Optimize Your Business With EDI Integration. Schedule a Consultation With Our Experts
What is EDI integration?
The EDI integration process creates an EDI workflow between the trading partners. It includes the selection of different steps and options within the EDI integration and determines the EDI standard, protocol type, documents, transactions, endpoints you would want to use, and the trading partners that you exchange information with. Once these elements have been pinpointed, the right time would be to make the best choice among the EDI systems that are available, whether you want to develop and operate an EDI platform yourself or get it from a third-party expert.
Stages for integrating EDI
B2B EDI integration requires multiple processes. Here’s a brief overview of the most common ones and how selecting the appropriate answer might make it easy for you to cross them off your to-do list.
1. Fulfilling prerequisites
Make sure the system you select has connections to numerous trading partners to streamline your EDI integration. In this manner, you can satisfy their expectations without having to do the laborious work of writing code. Rather, since your electronic data interchange services provider will have already accomplished the bulk of the work, you can just connect to their platform and get going.
2. Examining your ERP configuration
Make sure an EDI partner has a standard enterprise EDI ERP connection with the most popular accounting apps and ERP systems before choosing one. By taking this step, you will know how your system handles data.
3. Determining what activities to trigger
It will be up to you to determine what actions warrant an EDI transaction. Make sure the EDI vendor’s platform makes this process as easy as possible for you while you are comparing prices. In other words, make sure you don’t need to write code to accomplish this.
4. Data extraction
Selecting a cloud-based EDI will simplify this process considerably. You should be able to easily extract and share financial data, contact details, and other essential data with your trading partners if you have the appropriate solution.
5. Data mapping
The process of converting EDI data into other forms for use with other apps and your ERP system is known as EDI mapping. This allows messages to be converted into digital documents. The data will be automatically mapped to the required EDI file format by the appropriate cloud-based EDI solution.
6. Notification testing
It is necessary to send out transmissions to your trading partners to let them know that you will be testing your EDI system. An application programming interface is ideally used to verify the validity of your data before exchanging it with a business partner. This is possible with some EDI integration solutions.
7. Examining
You can start testing after notifying your trading partners. Your EDI integration software should ideally allow you to perform your testing whenever it’s convenient for you. In this manner, you may ascertain whether you are fulfilling the needs of your partners and receive prompt feedback regarding the effectiveness of your test.
8. Activating
It’s time to go live with your EDI integration once it has been configured and tested successfully. When you’re ready, set, and go, this can happen with the correct cloud-based EDI solution!
Selecting the Best EDI Solution Type for You
There isn’t a single EDI service that works for every company, so choosing the best one might be difficult. You can adapt one to your particular needs to ensure it works best for you. There are numerous options to use, such as managed, unmanaged, cloud-based, on-premises, and web-based. Choosing the right option to use can be overwhelming.
On-Premise vs Cloud
The cloud-based EDI software is kept on the servers of your EDI vendor. The on-premise EDI integration software installation is done on the servers of your business. Software-as-a-Service is just one of many common names for cloud-based software. This software requires absolutely no personal management or upkeep. By using the internet, you can get the program on-demand and essentially “rent” it from the vendor. You save time and money since the vendor takes care of upgrades, updates, and problem fixes. However, the management load associated with on-premises software is higher. However, since your business “owns” the solution, you have complete control over its customization and can do as you choose.
Managed Vs. Unmanaged
Everything is taken care of for you when you use a managed EDI solution, including data mapping, onboarding, and continuous administration and monitoring of your EDI operations. Not a single finger needs to be lifted. When a solution is not handled, you are left to handle everything on your own. You should choose a managed solution if you anticipate large document volumes, have a complicated back-office system to integrate, or are unable to handle EDI on your own. Just be sure that, should the need arise in the future, you can simply bring everything back in-house!
Web-Based EDI
For businesses that anticipate exchanging less than 200 documents per month with fewer than five trading partners, web-based EDI is a low-cost option. This eliminates the need for back-office integration, allowing for fast implementation of these solutions. Easy-to-read websites present EDI data from business partners, and a straightforward browser interface allows you to respond.
Methods of Integration
There are various approaches to implementing EDI integration methods, each with pros and downsides of their own:
Direct EDI Integration: In this EDI integration methods approach, your system and the systems of your trading partners are connected directly. While offering exceptional speed and control, setting up and maintaining [subject] can be complex and costly.
Value-Added Networks (VANs): VANs manage EDI communications between firms by serving as middlemen. They provide security and dependability, which facilitates communication with several commercial partners without requiring direct connections.
AS2: The widely used AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) protocol allows for safe EDI communication over the Internet. To guarantee secure data transport, it makes use of digital certificates and encryption. AS2 is frequently useful in sectors like retail and healthcare that demand safe transactions.
By facilitating real-time data interchange between systems, APIs offer a contemporary solution to EDI. Businesses wishing to integrate EDI with many platforms and apps will find EDI integration methods incredibly adaptable as they can handle a variety of data formats.
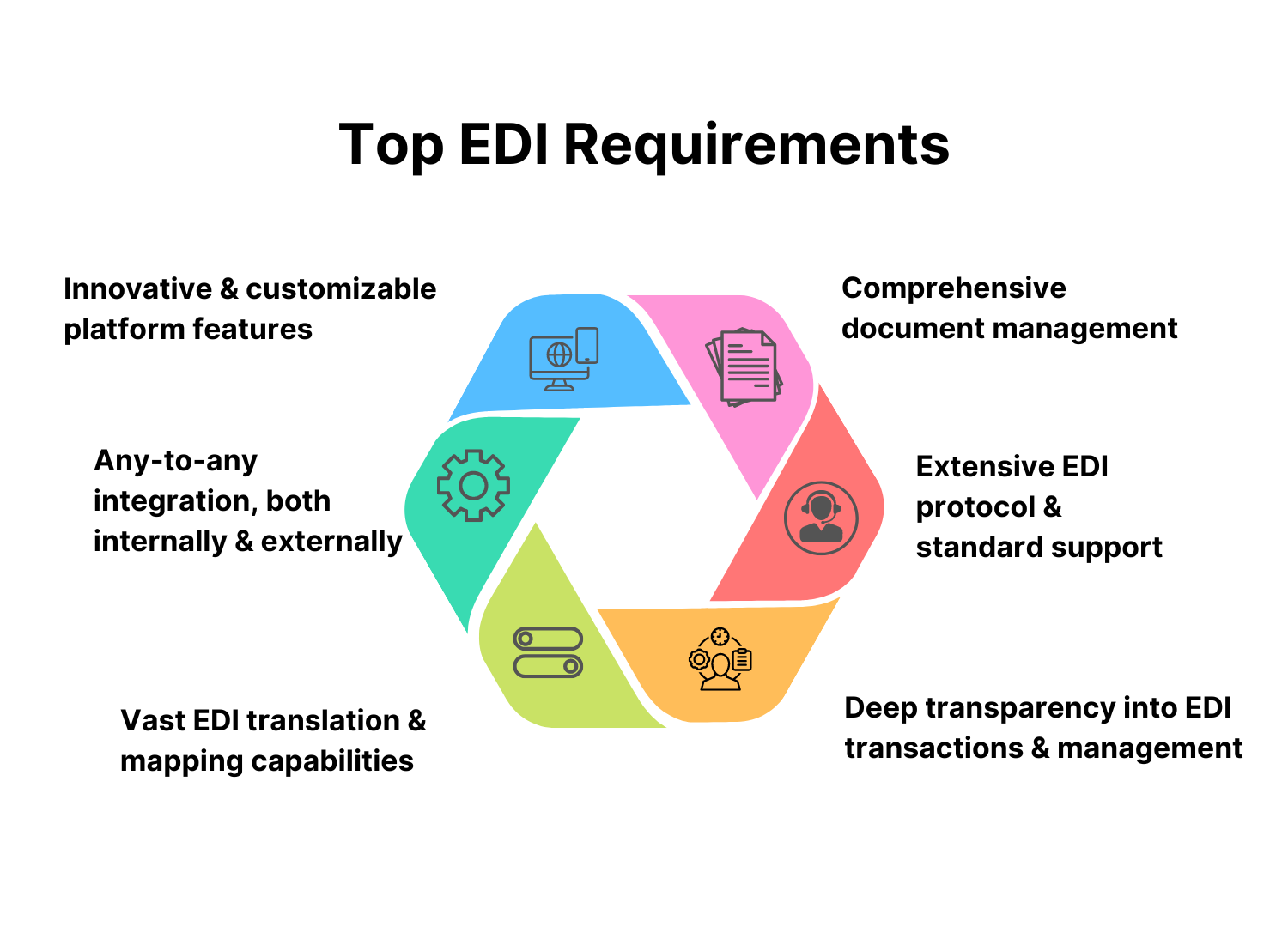
Requirements for EDI Integration
Successful EDI integration methods implementation necessitates careful planning and consideration of numerous needs. The optimal EDI integration methods for your company will rely on some variables, including:
- How many trading partners do you have?
- The amount of EDI transactions that you handle
- Your resources and technical know-how
- Your spending plan
- Preferences of your trading partners
From the standpoint of project management, an EDI integration method must complete five essential stages:
1. Organizing and Practicality:
- Establish project goals and objectives: This entails stating the intended results and advantages of EDI integration methods for your company.
- Do a feasibility study: This evaluates the project’s organizational, financial, and technical viability while taking resources, spending limits, and probable difficulties into account.
- Create a project schedule: Timelines, roles, and responsibilities, communication procedures, identification of potential risks, and risk mitigation techniques are all included in this.
2. Configuration and Design:
- Select an EDI supplier: Careful thought must go into selecting the best EDI supplier. You may ensure the success of your EDI integration project by carefully assessing your needs, investigating your possibilities, and ranking your long-term objectives.
3. Design and Examination:
- Create any unique integration solutions that are required. This could entail changing current applications to accept EDI data or creating interfaces between your internal systems and the EDI solution.
- Do extensive testing: To guarantee accuracy, security, and interoperability, test data interchange with all trading partners.
- Refine and troubleshoot: Examine test findings, find and fix any mistakes or inconsistencies, and adjust settings to maximize efficiency.
4. Training and Deployment:
- Put the system into regular usage with your trading partners by going live with EDI connectivity.
- Educate and assist users: All employees participating in the new electronic data interchange training procedures should receive thorough training, as well as continuing assistance and technical support for troubleshooting.
- Analyze and monitor: To maximize efficacy and meet changing needs, continuously assess data exchange performance, spot possible problems, and make necessary adjustments.
5. Upkeep and Enhancement:
- Carry out routine maintenance and upgrades on the system: Make that the integrations and EDI solution continue to work with the most recent versions of the software and the needs of trading partners.
- Evaluate and optimize: To find areas for improvement and streamline procedures for greater effectiveness and cost savings, regularly examine performance indicators and user input.
- Expansion and adaptation: As your company develops, think about expanding the EDI system to incorporate more trading partners or document formats.
The road map for a successful EDI integration method consists of these five steps. Through strict adherence to these guidelines and customization to your particular project needs, you may reduce risks, optimize effectiveness, and enjoy the whole advantages of EDI integration for your company.
Top Techniques for a Smooth Implementation
Take into account the following best practices to guarantee seamless EDI integration methods:
- Arrange Completely: Create a thorough implementation plan that specifies the procedures, timetable, and materials needed. Provide backup plans in case there are difficulties or delays.
- Engage Stakeholders: From the beginning, involve all pertinent parties, such as trading partners, IT, operations, and finance. For implementation to be effective, their support and input are essential.
- Perform Testing: Make sure the EDI system functions properly and that data is exchanged appropriately by conducting thorough testing before going live. End-to-end testing with your trading partners ought to be part of this.
- Provide Training: See to it that the new EDI system is adequately explained to your team. They will be better able to comprehend the procedures and equipment used, which will lower the possibility of mistakes and increase productivity.
- Monitor and Improve: Following installation, keep an eye on your EDI system’s functionality at all times. To determine areas that require improvement, get input from users and trading partners, and adjust the system as necessary.
Although effective EDI implementation necessitates thorough planning, EDI benefits through appropriate integration solutions, and continuing support, the advantages in terms of accuracy and efficiency make the investment worthwhile.
Future Trends and Innovations in EDI Integration
New Technologies Affecting the Integration of EDI
The EDI integration methods are always evolving, with new technologies offering to provide capabilities for operational optimization. The growth of e-commerce and its impact on EDI is one significant trend.
With the expansion of e-commerce, it finds valuable uses of EDI to manage such high volumes of business transactions and enhance order processing and fulfillment operations. An e-commerce company can thereby automate and standardize data interchange with suppliers, warehouses, and shipping companies. It thus ensures quicker and error-free transaction processing using EDI.
Blockchain is another technological advancement that is significantly influencing EDI integration. It can be a vital supplement to the use of EDI since it is effective with data security, transparency, and traceability. Blockchain creates unchangeable transaction records, which can aid in reducing fraud and preserving data integrity during exchange. Protocols like these are crucial for sectors like finance and supply chain, where accurate data communication is vital.
Forecasts Regarding the Future of EDI
For EDI, the future is bright as long as technology keeps getting better. Cloud-based EDI solutions are flexible, scalable, and economical, so the adoption of cloud-based EDI is one of the key trends that will decide the future direction of the technology. Cloud-based platforms make EDI available and affordable for all sizes of companies; these facilitate real-time data interchange and B2B connectivity with other cloud services.
The growing usage of APIs for EDI integration methods is a further prediction. APIs enable more flexible and efficient data exchange than traditional EDI. This kind of change can, among other things, help EDI better meet the particular needs of companies and their trading partners.
Techniques for Maintaining Your Edge in a Changing Environment
Within the fast-moving EDI market, the only way for businesses to get ahead is to think and act proactively. Keeping up with the latest technological and industry developments supports this process. Training and development can ensure IT and operations teams are ready for new technology.
Companies ought to collaborate with the most creative EDI service providers, who lead the way in technological breakthroughs. In the end, these suppliers can offer the knowledge, resources, and assistance required to coordinate the intricacy of EDI integration and solution deployment.
Ultimately, a business can adapt and seize new possibilities quickly if it cultivates a culture of adaptability and continual improvement. Maintaining a competitive edge will require accepting new technology with openness, asking trading partners for feedback, and routinely assessing and streamlining EDI documents and procedures.
In conclusion
We examined the revolutionary possibilities of EDI integration in this extensive book, including its historical relevance, essential elements, and shared standards. We emphasized how EDI can boost workflow productivity, lower manual error rates, and improve supply chain management by providing real-time visibility.
Along with tactics for resolving typical obstacles, the practical components of implementing EDI were also covered. These included evaluating organizational preparedness, choosing appropriate integration platform solutions, and adopting best practices.
Business growth depends on EDI integration because it lowers costs, simplifies processes, and strengthens bonds with trading partners. Enterprise Data Interchange solutions boost overall business efficiency and competitiveness by automating data transfers and guaranteeing accurate, timely information flow.