Table of Contents
In today’s increasingly digitized business landscape, cybersecurity remains a paramount concern for organizations of all sizes. As cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring secure access to critical systems and applications is imperative. Amidst this backdrop, the adoption of Enterprise Password Management Software emerges as a fundamental strategy for businesses to fortify their cybersecurity posture and protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
According to a study conducted by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 amounted to $4.24 million, with an average of 290 days to identify and contain the breach. This alarming statistic underscores the critical importance of implementing effective password management practices to mitigate the financial and reputational damages resulting from cyber incidents.
In addition to protecting against external threats, Enterprise Password Management Software. It also addresses internal risks posed by employee negligence or malicious intent. According to a report by Verizon, insider threats account for approximately 34% of all data breaches, highlighting the need for custom enterprise software development companies to implement robust access controls and monitoring mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
Furthermore, with the proliferation of remote work and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies. The need for secure password management solutions becomes even more pronounced. Enterprise Password Management Software enables organizations to enforce strong password policies, facilitate a secure software development framework with remote access, and ensure compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws.
Enterprise Password Management Software plays a pivotal role in safeguarding. Businesses against cyber threats and data breaches in 2025 and beyond. By implementing robust password management solutions, enterprise software development services can mitigate risks, enhance cybersecurity resilience, and safeguard their most valuable assets from unauthorized access and exploitation.
Introduction to Enterprise Password Management Software Solutions
Where cyber threats loom large and data breaches are increasingly prevalent. The need for robust password management solutions has never been more critical. Enterprise Password Management Software Solutions emerge as indispensable tools for custom software development companies in USA seeking to fortify their cybersecurity defences and safeguard sensitive information against unauthorized access.
Data from the 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report by the Ponemon Institute reveals that the average cost of a data breach amounted to $4.24 million, with an average of 290 days to identify and contain the breach. These staggering figures underscore the significant financial and reputational repercussions that businesses face in the event of a security incident.
Enterprise Password Management Software Solutions address this pressing challenge. By providing a centralized platform for securely storing, managing, and controlling access to passwords and credentials across an organisation’s network. Therefore, by implementing advanced encryption protocols and authentication mechanisms with artificial intelligence in software development, these solutions enable businesses to enhance password security and mitigate the risks associated with weak or compromised credentials.
Moreover, insider threats pose a significant risk to enterprise custom software development companies, accounting for approximately 64% of all data breaches, according to a report. Enterprise Password Management Software Solutions help mitigate internal risks by enforcing strong password policies and facilitating secure remote access. Therefore, monitoring user activity to detect and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Understanding The Role of Password Management Software in Modern Business Operations
1. Enhanced Security
Password management software provides robust encryption and security measures to protect sensitive credentials from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
2. Centralized Password Storage
It offers a centralized platform for securely storing and managing passwords, eliminating the need for users. However, to remember multiple passwords or resort to insecure methods of storing credentials.
3. Streamlined Access
Password management software enables users to access their passwords conveniently from any device or location. Moreover, by improves productivity and efficiency by 51% in modern business environments.
4. Strong Password Policies
It enforces strong password policies, such as requiring complex passwords and regular password changes. To enhance security and prevent password-related vulnerabilities for many custom software development consulting companies.
5. Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Many password management solutions offer MFA capabilities, adding an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification steps, such as biometric authentication or one-time passwords.
6. Audit Trails and Reporting
Password management software provides audit trails and reporting functionalities. Allowing administrators to track user activity by 30%, monitor password usage by 25%, and generate compliance reports.
7. Password Sharing and Collaboration
Some solutions facilitate secure password sharing and collaboration among custom software development outsourcing companies and team members, enabling seamless collaboration while maintaining security protocols.
8. Integration with Identity and Access Management (IAM) Systems
Password management software can integrate with IAM systems, providing organizations with comprehensive control over user access rights and permissions.
Don’t Compromise On Security. Invest in Our Enterprise Password Management Software for Comprehensive Protection.
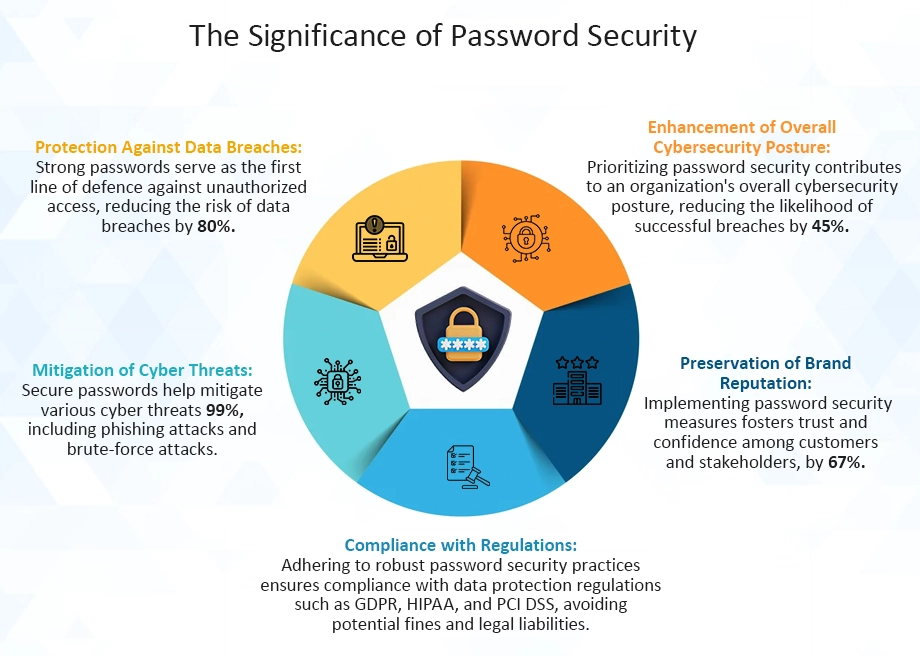
Importance of Robust Password Security Measures in Safeguarding Sensitive Data
1. Protection Against Unauthorized Access
Robust password security measures act as the first line of defence against unauthorized access to sensitive data and confidential information.
2. Prevention of Data Breaches
Implementing strong password security measures helps prevent data breaches caused by compromised or weak passwords, reducing the risk of costly security incidents and reputational damage.
3. Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
Many regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR and HIPAA, mandate the implementation of robust password security measures. Therefore, to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
4. Safeguarding Customer Trust
By implementing strong password security measures, digital transformation services demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer data and enhancing trust and confidence among clients and stakeholders.
5. Mitigation of Insider Threats
Strong password security measures help mitigate insider threats by limiting access to sensitive data based on user roles and permissions. It therefore helps in reducing the risk of data leaks or unauthorized disclosures.
6. Protection of Intellectual Property
Robust password security measures safeguard intellectual property and proprietary information from theft or unauthorized access, preserving the competitive advantage of businesses and preventing financial losses.
7. Prevention of Credential Stuffing Attacks
Strong password security measures help prevent credential stuffing attacks, where attackers use compromised credentials to gain unauthorized access. For accounts and systems, this leads to potential data breaches and financial losses.
8. Reduction of Operational Risks
Implementing strong password security measures reduces operational risks associated with password-related vulnerabilities, such as unauthorized access, data loss, and system downtime, improving overall system security posture.
Exploring The Importance of Password Security in Modern Business Environments
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, password security stands as a cornerstone in safeguarding sensitive data and protecting against cyber threats. As businesses increasingly rely on digital platforms for operations and communication. The importance of robust password security practices cannot be overstated. Let’s explore the critical role that password security plays in modern custom software development outsourcing environments.
- Data Protection: Strong passwords are the first defence against unauthorized access to sensitive information, shielding businesses from data breaches and cyber-attacks.
- Compliance Requirements: Many industries have stringent regulatory requirements mandating secure password practices to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data.
- Preventing Unauthorized Access: Password security measures help prevent unauthorized individuals from gaining access to confidential business systems, applications, and resources.
- Safeguarding Customer Trust: By implementing strong password security measures, businesses demonstrate their commitment to protecting customer data, and fostering trust and loyalty.
- Mitigating Financial Losses: Weak passwords can lead to financial losses due to data breaches, legal liabilities, and reputational damage, highlighting the financial impact of inadequate password security.
- Employee Accountability: Implementing password policies and guidelines promotes employee accountability for maintaining secure passwords and adhering to company security protocols.
- Cybersecurity Awareness: Educating employees about the importance of password security enhances cybersecurity awareness within enterprise custom software development companies, empowering individuals to recognize and respond to potential threats.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Employing multi-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security beyond passwords, enhancing protection against unauthorized access attempts.
Risks Associated with Weak Password Practices
Weak password practices pose significant risks to businesses, leaving them vulnerable to cyber threats and potential data breaches. In today’s interconnected digital landscape, where sensitive information is stored and transmitted online. However, the importance of robust password security cannot be overstated. Let’s delve into the risks associated with weak password practices and their potential impact on custom software development services USA.
- Increased Vulnerability to Cyber Attacks: Weak passwords, such as simple or easily guessable combinations, create an open invitation for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities and gain unauthorized access to sensitive systems and data.
- Data Breaches and Compromised Confidentiality: Inadequate password security increases the likelihood of data breaches, leading to the compromise of confidential information, including customer data, financial records, and intellectual property.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance Risks: Businesses that fail to implement adequate password security measures may face legal and regulatory consequences, including fines, penalties, and reputational damage, for non-compliance with industry-specific regulations and data protection laws.
- Financial Losses and Business Disruption: The aftermath of a data breach can result in substantial financial losses for businesses, stemming from legal expenses, regulatory fines, remediation costs, and loss of customer trust, as well as potential disruptions to operations and revenue streams.
- Reputational Damage and Loss of Trust: A data breach resulting from weak password practices can tarnish a business’s reputation and erode customer trust, leading to long-term consequences, such as diminished brand loyalty, negative publicity, and loss of competitive advantage in the market.
Impact of Password Breaches on Business Operations and Reputation
Password breaches have become increasingly prevalent in today’s digital landscape, posing significant challenges to businesses worldwide. Beyond the immediate security implications, these breaches can have far-reaching consequences that extend to both healthcare digital transformation companies‘ operations and reputations. Let’s explore the impact of password breaches on business operations and reputation, along with the data that underscores their significance.
- Disruption of Business Continuity: Password breaches can disrupt business operations, leading to downtime, productivity losses, and disruptions in service delivery. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the average cost of downtime resulting from a data breach is $5.3 million.
- Financial Losses and Remediation Costs: Businesses incur significant financial losses and remediation expenses in the aftermath of a password breach, including incident response, forensic investigation, and legal fees. The Ponemon Institute’s research indicates that the average total cost of a data breach is $3.86 million.
- Damage to Customer Trust and Loyalty: Password breaches erode customer trust and loyalty, as affected individuals may lose confidence in the custom enterprise software development companies’ ability to protect their personal information. According to a survey by Gemalto, 70% of consumers would stop doing business with a company following a data breach.
- Reputational Damage: Password breaches can tarnish a business’s reputation, leading to negative publicity, brand devaluation, and long-term damage to its image. The 2023 Edelman Trust Barometer revealed that 57% of consumers have lost trust in businesses due to how they handle data breaches.
- Regulatory Compliance Concerns: Password breaches may trigger regulatory compliance requirements, exposing custom software development consulting companies to potential fines, penalties, and legal liabilities for non-compliance. The European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual turnover for data breaches.
Features and Benefits of Enterprise Password Management Software
Enterprise password management software plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information and enhancing security measures within organizations. As businesses increasingly rely on digital platforms for operations and communication. The need for robust password management solutions has become paramount. Let’s explore the features and benefits of enterprise password management software and its significance in modern business environments.
- Centralized Password Storage: Enterprise password management software offers a centralized platform for securely storing and managing passwords, eliminating the need for manual and fragmented password management practices.
- Strong Password Generation: These software solutions facilitate the creation of strong, complex passwords using random character combinations, ensuring enhanced security and resilience against password-related attacks.
- Secure Password Sharing: With enterprise password management software, authorized users can securely share passwords with colleagues or team members, streamlining collaboration while maintaining data confidentiality.
- Role-Based Access Control: These solutions enable organizations to implement role-based access control, allowing administrators to define and enforce access permissions based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication Integration: Many enterprise password management software solutions offer integration with multi-factor authentication (MFA) methods, adding an extra layer of security to password-protected accounts and systems.
- Auditing and Reporting Capabilities: These software solutions provide robust auditing and reporting features, allowing administrators to monitor password usage, track access history, and generate compliance reports for regulatory purposes.
Overview of Key Features Offered by Password Management Solutions
Let’s explore the key features offered by these solutions and their significance in modern business environments.
- Centralized Password Storage: Password management solutions provide a centralized repository for securely storing and organizing passwords, eliminating the need for disparate spreadsheets or insecure storage methods.
- Strong Password Generation: These solutions include built-in password generators that create strong, complex passwords using random characters, digits, and symbols, bolstering security against brute force attacks.
- Secure Password Sharing: Many password management solutions offer secure password-sharing functionality, allowing users and many custom software development outsourcing companies to safely share passwords with authorized individuals or teams without compromising confidentiality.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Integration: Advanced password management solutions support integration with multi-factor authentication methods, adding an extra layer of security to password-protected accounts and systems.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): RBAC features enable administrators to assign granular access permissions based on user roles and responsibilities, ensuring that users only have access to the passwords and resources they need.
- Password Policy Enforcement: These solutions enforce password policies, such as minimum length, complexity requirements, and expiration periods, to promote adherence to security best practices and regulatory standards.
Benefits of Centralized Password Storage, Encryption, and Secure Sharing
In today’s interconnected digital landscape, where sensitive information is stored and transmitted online. Effective password management is essential for safeguarding data and protecting against cybersecurity threats. Centralized password storage, encryption, and secure sharing are key features offered by password management solutions. That plays a critical role in enhancing security and streamlining password management processes within custom software development companies in USA. Let’s explore the benefits of these features and their significance in modern business environments.
- Enhanced Security: Centralized password storage ensures that passwords are securely stored in a single, encrypted database, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches compared to scattered and insecure storage methods.
- Simplified Management: With centralized password storage, administrators can easily manage and organize passwords from a central dashboard, streamlining password management processes and improving overall efficiency.
- Improved Compliance: Centralized password storage solutions often include features to enforce password policies and regulatory compliance requirements, ensuring that passwords adhere to security best practices and industry standards.
- Reduced Password Fatigue: Centralized password storage eliminates the need for users to remember multiple passwords for different accounts, reducing password fatigue and the likelihood of using weak or easily guessable passwords.
- Enhanced Encryption: Password management solutions use strong encryption algorithms to encrypt password databases, protecting sensitive credentials from unauthorized access or disclosure in the event of a security breach.
- Secure Sharing: Secure sharing features allow authorized users to securely share passwords with colleagues or team members without compromising confidentiality, facilitating collaboration while maintaining data security.
- Auditing and Monitoring: Centralized password storage solutions often include auditing and monitoring features that enable administrators to track password usage, monitor access history, and generate compliance reports for regulatory purposes for many healthcare digital transformation companies.
Risks of Poor Password Management Practices in Businesses
In an era where cybersecurity threats loom large and data breaches are increasingly common. The importance of robust password management practices cannot be overstated. Businesses today rely heavily on digital platforms and networks to conduct operations, store sensitive information, and interact with customers. However, with this increased reliance comes the heightened risk of cyberattacks. Many of these are facilitated by poor password management practices. From weak passwords to lax authentication protocols, businesses face a myriad of risks when they neglect to prioritize effective password management.
- Data Breaches: Weak or easily guessable passwords provide cybercriminals with a gateway to access sensitive company data. According to the 2021 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report, 61% of data breaches involved credential data. Highlighting the critical role passwords play in cybersecurity.
- Account Takeovers: Inadequate password management can lead to unauthorized access to employee accounts. Allowing cyber attackers to infiltrate internal systems, impersonate staff, and carry out fraudulent activities. According to the Identity Theft Resource Center, account takeovers accounted for 20% of reported data breaches in 2023.
- Financial Losses: Cyberattacks resulting from poor password management practices can have severe financial repercussions for custom software development consulting companies. The average cost of a data breach was $4.24 million in 2021, as reported by IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report. Encompassing expenses related to incident response, regulatory fines, legal fees, and reputational damage.
- Reputational Damage: A data breach resulting from compromised passwords can erode customer trust and tarnish a company’s reputation. According to a survey by Kaspersky Lab, 47% of consumers would stop using a business’s services if they were affected by a data breach. Underscoring the importance of maintaining secure password practices to safeguard brand integrity.
Common Vulnerabilities Associated with Manual Password Management
1. Weak Passwords
Manual password management often leads to the use of weak or easily guessable passwords. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), commonly used passwords such as “password” or “123456” remain prevalent despite being highly vulnerable to brute-force attacks. A study by the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) found that “123456” was the most commonly breached password in 2020, highlighting the persistence of this vulnerability.
2. Password Reuse
With manual password management, individuals tend to reuse passwords across multiple accounts, increasing the risk of credential-stuffing attacks. Cybercriminals leverage compromised credentials from one platform to gain unauthorized access to other accounts associated with the same password. According to Google’s research, 52% of users reuse the same password for different accounts, exacerbating the security implications of password reuse.
3. Lack of Regular Updates
Manual password management often results in infrequent password updates, leaving accounts vulnerable to exploitation over time. Employees may neglect to change passwords regularly or fail to adhere to password expiration policies set by enterprise custom software development companies. A survey conducted by the Ponemon Institute found that 69% of users admit to sharing passwords with others in the workplace. Indicating a lack of emphasis on regular password updates and security hygiene.
4. Insecure Storage Methods
Users commonly store passwords insecurely, such as in unencrypted text files, sticky notes, or spreadsheets, when managing them manually. This practice increases the risk of unauthorized access, especially if physical documents are lost or stolen. A report by LastPass revealed that 50% of respondents store passwords insecurely, with 27% using physical documents and 20% relying on unsecured digital files.
5. Susceptibility to Social Engineering
Manual password management is susceptible to social engineering tactics, where attackers manipulate individuals. Into disclosing sensitive information such as passwords through deception or coercion. Employees may fall victim to phishing emails, phone calls, or pretexting scams, compromising their credentials. Verizon’s 2021 Data Breach Investigations Report identified social engineering as a factor in 36% of data breaches. Therefore, by underscoring the significance of this vulnerability in password security.
6. Limited Password Complexity Enforcement
Manual password management lacks the robustness of automated systems in enforcing password complexity requirements. Users may opt for simple passwords that are easy to remember but lack sufficient complexity to resist brute-force or dictionary attacks. According to a survey by Varonis, 61% of organizations have no policies in place. To enforce password complexity, leaving them vulnerable to exploitation of weak passwords.
7. Difficulty in Password Sharing Management
In collaborative environments, manual password management complicates the sharing of credentials among team members while maintaining security. Custom software development outsourcing may resort to insecure methods of sharing passwords, such as email or messaging platforms, risking unauthorized access. A survey by LogMeIn found that 61% of employees share passwords with coworkers. Highlighting the challenge of managing password sharing securely in manual systems.
8. Lack of Accountability and Auditing
Manual password management makes tracking and auditing password-related activities difficult. Leading to a lack of accountability for security breaches or unauthorized access incidents. Without proper logging and monitoring mechanisms, organizations struggle to identify and mitigate security threats effectively. The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report revealed that 31% of breaches involved privilege misuse. Highlighting the importance of accountability in password management to prevent insider threats.
Addressing these vulnerabilities requires custom software development consulting companies to transition from manual password management practices to automated solutions that offer enhanced security, usability, and accountability. Implementing measures such as multi-factor authentication, password managers, and regular security awareness training. That can significantly mitigate the risks associated with manual password management.
Choosing The Right Enterprise Password Management Solution
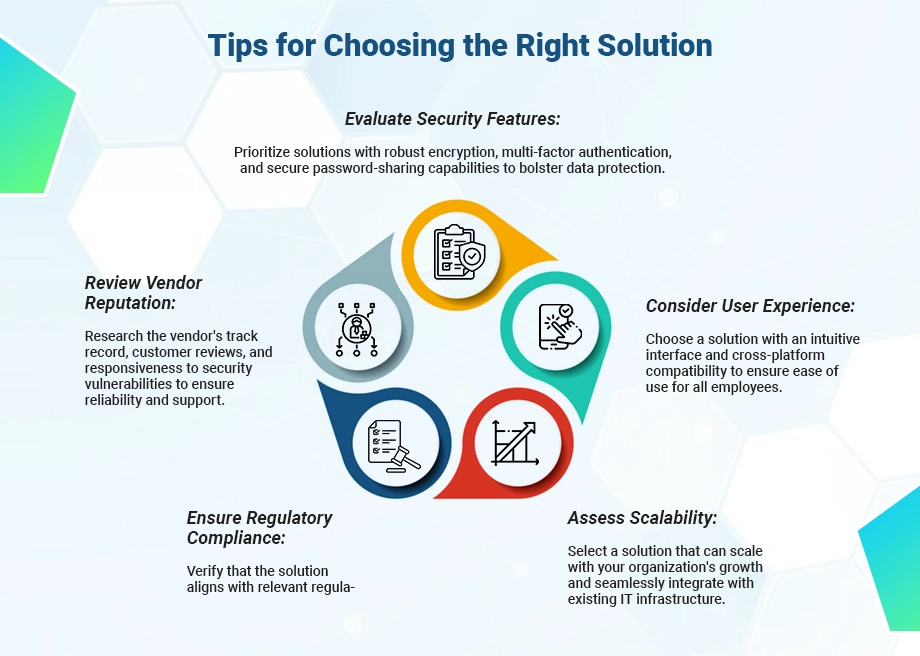
Cyber threats continue to evolve and data breaches pose significant risks to businesses. Selecting the right enterprise password management software solution is paramount. With the proliferation of digital assets, applications, and user accounts within custom enterprise software development companies, the need for robust password management practices has never been more critical. However, choosing the appropriate solution requires careful consideration of factors. Such as security features, usability, scalability, and integration capabilities to effectively mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive information.
1. Security Features
Look for password management solutions that offer strong encryption protocols to protect stored passwords from unauthorized access. AES 256-bit encryption is considered a gold standard in encryption technology. Ensure the solution supports multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security beyond passwords. Reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised. Evaluate whether the solution offers features such as password strength assessment. Password expiration reminders, and secure password-sharing options to enhance overall security posture.
2. Usability and User Experience
Prioritize solutions with intuitive user interfaces and seamless user experiences to encourage adoption and compliance among employees. Consider solutions that offer cross-platform compatibility, allowing users to access. To manage passwords across various devices and operating systems with ease. Look for features like browser extensions and mobile applications. That streamlines password management tasks and facilitates secure access to accounts on the go.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
Assess the scalability of the password management solution to accommodate the evolving needs of your organization as it grows and expands. Ensure the solution can integrate seamlessly with existing IT infrastructure. Identity management systems and cloud-based applications. To facilitate centralized management and provisioning of passwords. Look for customizable features and policy settings that align with your enterprise software development company’s unique security requirements and compliance mandates.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
Ensure the chosen password management solution complies with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOC 2 to avoid potential legal and financial implications. Evaluate whether the solution offers audit trails, reporting capabilities, and compliance management features. To demonstrate adherence to regulatory mandates and facilitate compliance audits.
5. Vendor Reputation and Support
Research the reputation and track record of the password management solution provider. Including their experience in the cybersecurity industry and customer satisfaction ratings. Consider factors such as the vendor’s responsiveness to security vulnerabilities, frequency of software updates, and quality of customer support services to ensure timely assistance and resolution of issues.
6. Cost and Value Proposition
Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) of the password management solution. Including licensing fees, implementation costs, training expenses, and ongoing maintenance fees. Consider the value proposition offered by the solution in terms of security benefits, productivity gains, and potential cost savings derived from reduced security incidents and streamlined password management processes.
7. Integration Capabilities
Assess the solution’s integration capabilities with other cybersecurity tools and platforms, such as single sign-on (SSO) solutions, identity and access management (IAM) systems, and security information and event management (SIEM) platforms. Look for open APIs and interoperability with third-party applications to facilitate seamless integration and interoperability within your organization’s IT ecosystem.
By considering these factors and conducting thorough due diligence, custom software development companies in USA can make informed decisions when selecting the right enterprise password management software solution that meets their security needs, enhances user productivity, and ensures compliance with regulatory requirements.
Implementing Best Practices for Password Security and Management
Implementing best practices for password security and management is imperative for enterprise software development services to safeguard their sensitive information and mitigate the risks of unauthorized access. Effective password security measures not only protect against external threats. But also help prevent insider breaches and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. By adhering to industry best practices and leveraging advanced security technologies. Therefore, businesses can strengthen their defences and foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness among employees.
1. Enforce Strong Password Policies
Require employees to create complex passwords comprising a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Set minimum password length requirements to ensure passwords are sufficiently robust and resistant to brute-force attacks. Implement password expiration policies to prompt users to change their passwords regularly, reducing the likelihood of password compromise.
2. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Augment password-based authentication with MFA to add an extra layer of security. Utilize factors such as biometrics, one-time passwords (OTP), smart cards, or hardware tokens to verify users’ identities. According to Microsoft, enabling MFA can block 99.9% of automated attacks.
3. Utilize Password Managers
Encourage employees to use password management tools to securely store and generate complex passwords. Password managers encrypt stored passwords and offer features like – password autofill and synchronization across devices. Research by the Ponemon Institute found that organizations using password managers experienced a 65% reduction in the cost of data breaches.
4. Educate Employees on Security Awareness
Provide comprehensive training on password security best practices, emphasizing the importance of creating strong passwords, avoiding password reuse, and recognizing phishing attempts. Conduct regular security awareness sessions to reinforce good password hygiene and educate employees about emerging threats. According to the 2023 State of Password Security report by LastPass, 66% of IT professionals from various custom software development services USA cite employee education as the most effective strategy for improving password security.
5. Implement Account Lockout Policies
Set account lockout thresholds to temporarily disable accounts after multiple failed login attempts, mitigating the risk of brute-force attacks. Configure lockout durations and reset procedures to prevent adversaries from repeatedly attempting to guess passwords. The SANS Institute recommends configuring account lockout policies to discourage password-guessing attacks effectively.
6. Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keep software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches to address vulnerabilities that could be exploited to steal passwords. Apply patches promptly to mitigate the risk of exploitation by malicious actors seeking to compromise password security. The Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that 60% of data breaches were attributed to vulnerabilities for which patches were available but not applied.
7. Monitor and Audit Password-related Activities
Implement robust logging and monitoring mechanisms to track password-related activities, such as failed login attempts and changes to password settings. Regularly review audit logs to detect suspicious behaviour and potential security incidents, enabling timely response and mitigation. The 2021 Cybersecurity Insiders Insider Threat Report found that 45% of enterprise custom software development companies lack sufficient visibility into their privileged users’ activities, highlighting the need for enhanced monitoring.
8. Secure Password Transmission and Storage
Encrypt passwords during transmission over networks to prevent interception by eavesdroppers. Store passwords securely using industry-standard encryption algorithms and hashing techniques to protect against unauthorized access in the event of a data breach. The use of secure communication protocols such as HTTPS and SSL/TLS ensures the confidentiality and integrity of password data in transit.
Securing Remote Work Environments with Password Management Solutions
Securing remote work environments has become increasingly vital in the wake of the global shift towards remote and hybrid work models. Password management solutions play a pivotal role in fortifying the security posture of remote work environments. By addressing the challenges posed by distributed teams accessing sensitive corporate resources from various locations. These solutions offer centralized management of passwords, ensuring that employees adhere to strong password practices even when working remotely.
According to a report by Cybersecurity Insiders, 81% of organizations view password management as a critical component of their cybersecurity strategy. Especially in remote work scenarios. By implementing password management solutions, enterprise software development services can enforce password complexity requirements, enable multi-factor authentication (MFA), and facilitate secure password sharing among remote team members. Furthermore, these solutions help mitigate the risks associated with password-related security incidents. Such as data breaches and unauthorized access, which can have significant financial and reputational consequences for businesses.
Research by the Ponemon Institute indicates that organizations using password management solutions experience 65% lower costs associated with data breaches compared to those without such solutions. Moreover, password management solutions enhance user productivity in remote work environments. By simplifying password-related tasks and reducing the likelihood of account lockouts or password resets. As remote work continues to be a prevalent trend, software development services in US must prioritize the adoption of robust password management solutions to safeguard their remote workforce and protect sensitive corporate assets from evolving cybersecurity threats.
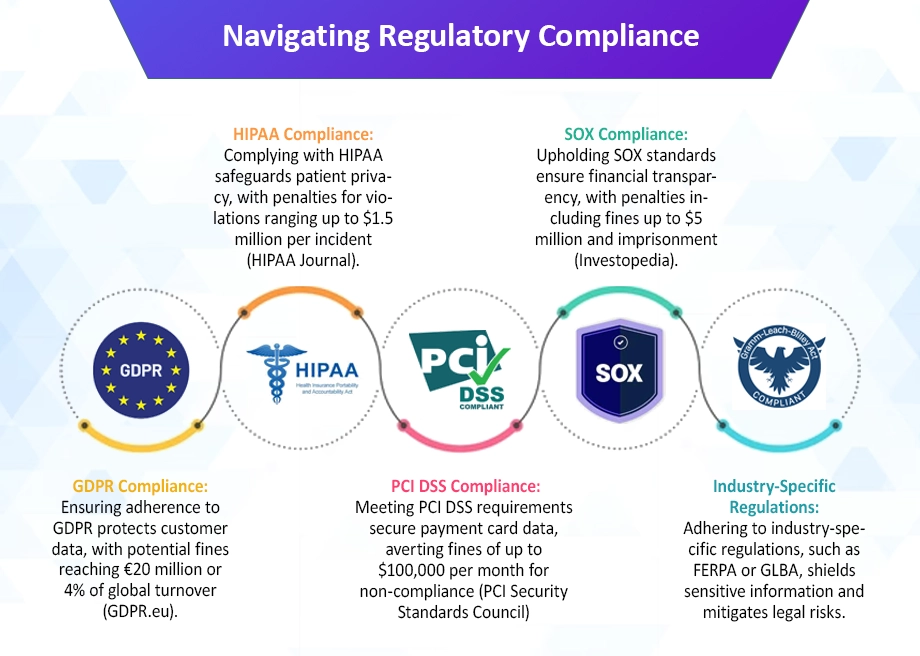
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations for Password Management
Compliance and regulatory considerations are paramount when implementing password management solutions to ensure adherence to industry standards and legal requirements. Various regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX). They mandate organizations to implement adequate safeguards for protecting sensitive data, including passwords.
For instance, GDPR requires custom enterprise software development companies to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of personal data, which includes the use of strong authentication mechanisms and encryption for passwords. Similarly, HIPAA mandates healthcare organizations to implement measures to protect electronic protected health information (ePHI). Including securing access to systems through robust password management practices. Non-compliance with these regulations can lead to severe penalties and fines.
According to the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of non-compliance with data protection regulations is $14.8 million. Highlighting the financial implications of failing to meet regulatory requirements. Therefore, custom software development companies in USA must ensure that their password management solutions align with applicable regulations, implement necessary controls to protect sensitive information, and regularly audit and report on compliance to regulatory authorities to mitigate the risk of penalties and reputational damage.
Conclusion: Safeguarding Your Business with Enterprise Password Management Software
The importance of robust password management cannot be overstated. As cyber threats continue to evolve and businesses increasingly rely on digital platforms for operations, the need for effective password security measures becomes paramount. Enterprise password management software offers a comprehensive solution to safeguard sensitive data and protect against cybersecurity threats.
By centralizing password storage, employing strong encryption, and facilitating secure sharing, password management software enhances security posture and streamlines password management processes within organizations. Studies have shown that businesses that implement password management solutions experience a significant reduction in the likelihood and impact of data breaches.
Furthermore, password management software provides auditing and monitoring capabilities. Enabling organizations to track password usage, monitor access history, and generate compliance reports. The agile software development life cycle not only helps ensure regulatory compliance but also provides valuable insights into password-related security incidents.
With the potential financial and reputational consequences of data breaches, investing in enterprise password management software. Therefore, it is a proactive measure to mitigate risks and safeguard business assets. According to research, the average cost of a data breach is estimated to be $4.24 million globally. It therefore highlights the financial impact of inadequate password security.
Enterprise password management software is a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, helping businesses protect sensitive information, maintain regulatory compliance, and mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats. By prioritizing password security, organizations can safeguard their business operations, reputation, and bottom line in today’s increasingly digital and interconnected world.
Take Control of Your Business’s Security Posture With Our Advanced Enterprise Password Management Solution.
Frequently Asked Questions about Enterprise Password Management Software
1. What is Enterprise Password Management Software, and How Does it Work?
Enterprise Password Management Software is a tool designed to securely store, organize, and manage passwords for various accounts and systems within enterprise software development services. It works by encrypting and centralizing passwords in a secure database. Allowing authorized users to access and retrieve passwords as needed. Additionally, it often includes features such as password generation, secure sharing, and auditing capabilities. To enhance password security and streamline password management processes.
2. How can Password Management Software Help Prevent Data Breaches?
Password Management Software helps prevent data breaches by enforcing strong password policies. Facilitating secure password sharing, and centralizing password storage in an encrypted database. Ensuring that passwords are complex, unique, and regularly updated, reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive accounts and systems. Additionally, it provides auditing and monitoring capabilities, allowing enterprise software development companies to track password usage, detect suspicious activities, and respond promptly to potential security threats.
3. What Features Should I Look for in An Enterprise Password Management Software Solution?
When selecting an Enterprise Password Management Software Solution, it’s essential to consider features. Such as centralized password storage, strong encryption, and multi-factor authentication integration. Also, secure password sharing, auditing and reporting capabilities, and cross-platform compatibility. These features ensure robust password security, streamline password management processes, and support compliance with regulatory requirements.
4. How can I Ensure the security of passwords stored in a Password Management System?
To ensure the security of passwords stored in a Password Management System, it’s crucial to implement best practices. Such as enforcing strong password policies, and regularly updating passwords. Enabling multi-factor authentication, restricting access to authorized users only, and regularly auditing password usage. Additionally, organizations should prioritize the security of the Password Management System itself. Therefore, by implementing encryption, access controls, and regular security updates.
5. What are The Best Practices for Implementing and Maintaining Password Management Solutions in My Organization?
Best practices for implementing and maintaining Password Management Solutions. These include conducting a thorough assessment of password security needs. Selecting a solution that meets those requirements, and educating users on password best practices. The proper use of the Password Management System, regularly auditing and updating passwords. Monitoring access logs for suspicious activities, and staying informed about emerging threats and security updates. Additionally, Custom Software Development Services USA should establish clear policies and procedures for password management and regularly review and update them as needed.






